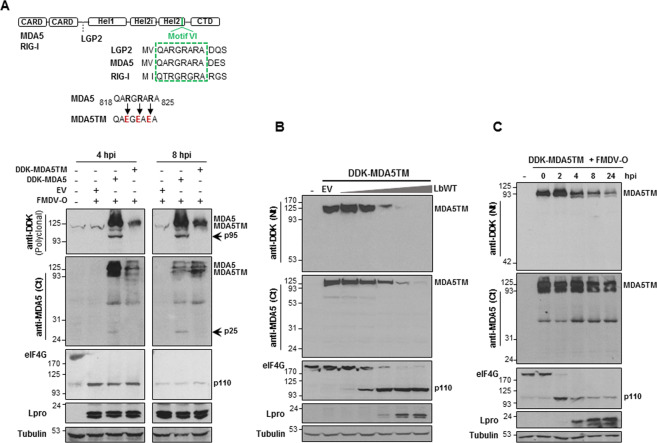
Fig. 6. MDA5TM is resistant to Lbpro cleavage during FMDV infection.
a A schematic representation of the three RLRs and the amino acid sequence of helicase motif VI, including residues modified in MDA5TM (R820E, R822E, R824E), are shown. SK6 cells were mock-transfected or transfected with 2 µg of DDK-MDA5, DDK-MDA5TM plasmids or an EV, then infected 24 h later with type-O FMDV at an MOI of 5 and lysed 4 or 8 h after infection. Lysates were analyzed by immunoblot for detection of the indicated proteins. In this case, a polyclonal anti-DDK antibody was used for detection of DDK-tagged MDA5 and MDA5TM. Arrows indicate the N- and C-terminal cleavage products of MDA5. The 110-kDa cleavage product of eIF4G is also depicted. b HEK293 cells were mock-transfected or co-transfected with 2 µg of a plasmid encoding DDK-MDA5TM and increasing amounts of LbWT plasmid (0.2, 2, 20, 200 and 2000 ng) or 2 µg of an EV. Cells were lysed 24 h later and analyzed by immunoblot for detection of the indicated proteins. c Swine SK6 cells were mock-transfected or transfected with 2 µg of a plasmid encoding DDK-MDA5TM and 24 h later infected with type-O FMDV at an MOI of 5. Cells were lysed at different times after infection and analyzed by immunoblot for detection of the indicated proteins as in b.