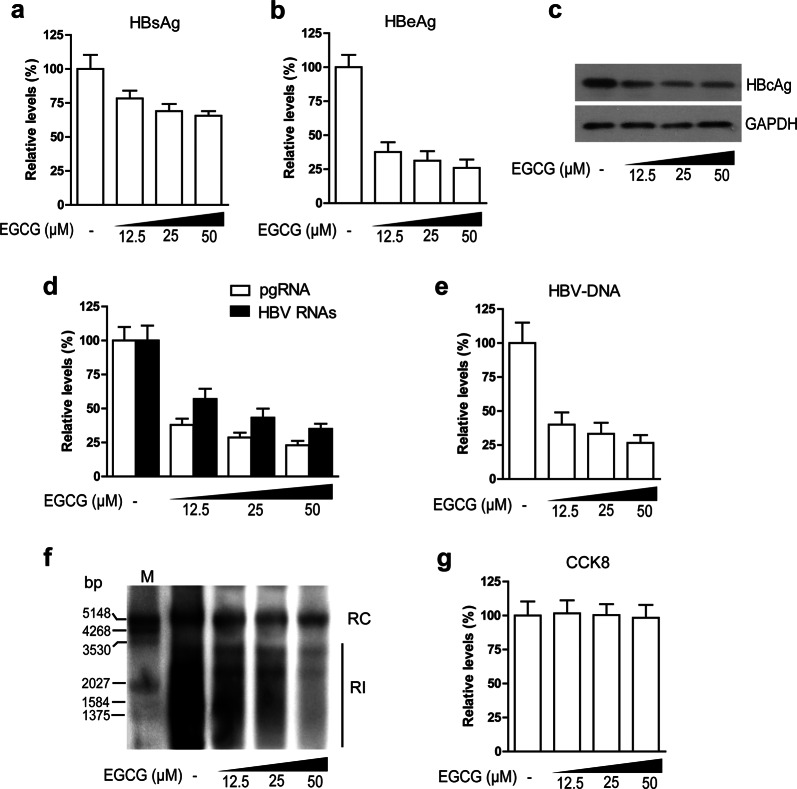
Fig. 1.
EGCG inhibited HBV gene expression and replication in HepG2.2.15 cells. HepG2.2.15 cells were treated with increasing amounts of EGCG (12.5, 25, 50 μM) for 24 h. The levels of HBsAg (a) and HBeAg (b) in culture supernatants were determined by ELISA; the level of HBcAg (c) in the cell lysates was determined by Western blotting; the levels of HBV pgRNA and HBV RNAs (d) were determined by qRT-PCR; the levels of intracellular core particle-associated HBV-DNA (e, f) were determined by quantitative real-time PCR and Southern blotting, respectively; and the cell viability (g) was determined by CCK8 assay. The values are expressed as the means ± SEM of three independent experiments