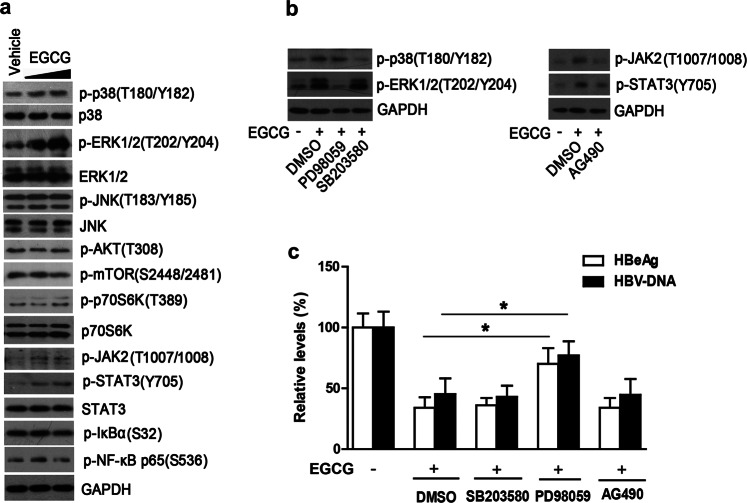
Fig. 3.
ERK1/2 signaling pathway was involved in the EGCG-mediated inhibition of HBV. a The effect of EGCG on the activation of the MAPK (p38, ERK, JNK), AKT/mTOR, and JAK2/STAT3 pathways. HepG2.2.15 cells were treated with increasing doses of EGCG (25 μM and 50 μM) for 24 h, and the cells were then subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. b The effect of pharmacological inhibitors on the activation of p38, ERK MAPK, or JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways. HepG2.2.15 cells were pretreated with the ERK inhibitor PD98059 (20 μM), the p38 inhibitor 203580 (10 μM) or the JAK2/STAT3 inhibitor AG490 (50 μM) for 1 h and then treated with 25 μM of EGCG for 24 h. The levels of p-p38, p-ERK, p-JAK2, or p-STAT3 were determined by Western blotting. c The role of p38, ERK MAPKs, or JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways in the EGCG-mediated inhibition of HBV. HepG2.2.15 cells were treated as in b, and the levels of HBeAg or HBV-DNA were determined by ELISA or qPCR, respectively. The values were expressed as the means ± SEM of three independent experiments; *P < 0.05 (unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t tests)