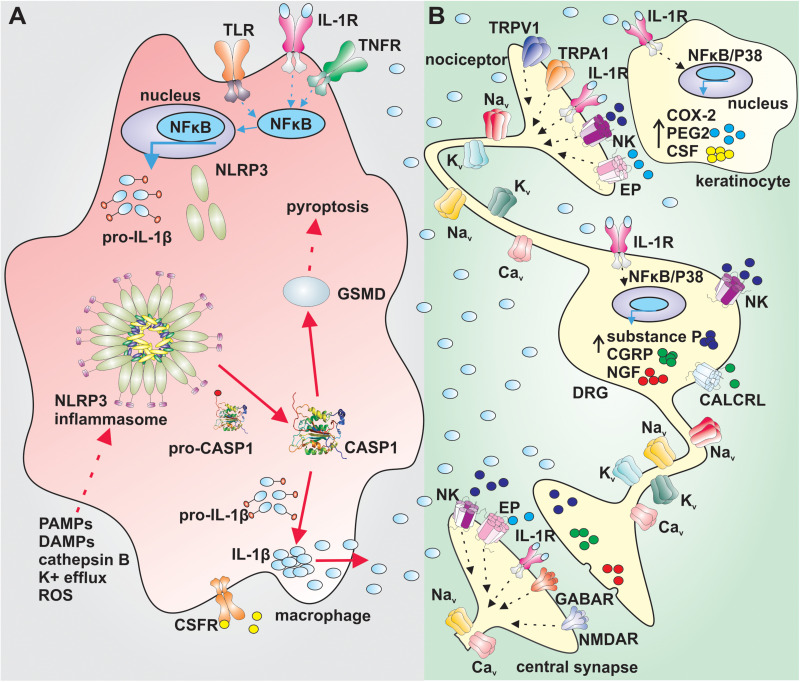
FIGURE 1.
Putative mechanism of sensory nerve sensitization by IL-1β. (A) Priming of the NLRP3 inflammasome via activation of TLRs, IL-1R or TNFR in NFκB dependent manner in macrophages leads to increased expression of NLRP3 and pro-IL1β (blue arrows). The canonical activation of the NLRP3 (red arrows) by PAMPs, DAMPs, cathepsin B, K+ efflux or ROS leads to assembly of the NLRP3 inflammasome complex, activation of CASP1 and cleavage of pro-IL-1β and GSMD. Active IL-1β is released by macrophages and exerts its effect via IL-1R on sensory nerves and surrounding cells. Active GSMD initiates pyroptosis. (B) IL-1β increases the gene expression of COX-2, PEG2, and CSF in keratinocytes in a NFκB/P38 mitogen kinase dependent manner. PEG2 sensitize peripheral nerves and CSF regulates differentiation, proliferation and survival of macrophages. IL-1β increases excitability of nociceptors by altering the function of tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channels via IL-1R and increases the gene expression in dorsal root ganglia in a NFκB/P38 mitogen kinase dependent manner. Substance P, CGRP, and NGF sensitize further peripheral nerves. IL-1β: interleukin 1β, TLR: toll-like receptor; IL-1R: interleukin-1 receptor; TNFR: tumor necrosis factor α receptor; NFκB: nuclear factor κB; NLRP3: NACHT, LRR, and PYD domains-containing protein 3; PAMPs: pathogen-associated molecular pattern; DAMPs: damage-associated molecular pattern; ROS: reactive oxygen species; CASP1: caspase 1; CSFR: colony-stimulating factor receptor; GSMD: gasdermin D; Nav: voltage gated sodium channel; EP: prostaglandin E receptor; NK: neurokinin receptor; CGRP: calcitonin gene-related peptide; CALCRL: calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor; NGF: nerve growth factor; COX-2: cyclooxygenase type 2; PEG2: prostaglandin E2; CSF: colony stimulating factor; NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; Kv: voltage gated potassium channel; Cav: voltage gated calcium channel; TRPV1: transient receptor potential channel vaniloid; TRPA1: transient receptor potential channel ankyrin; GABAR: gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor.