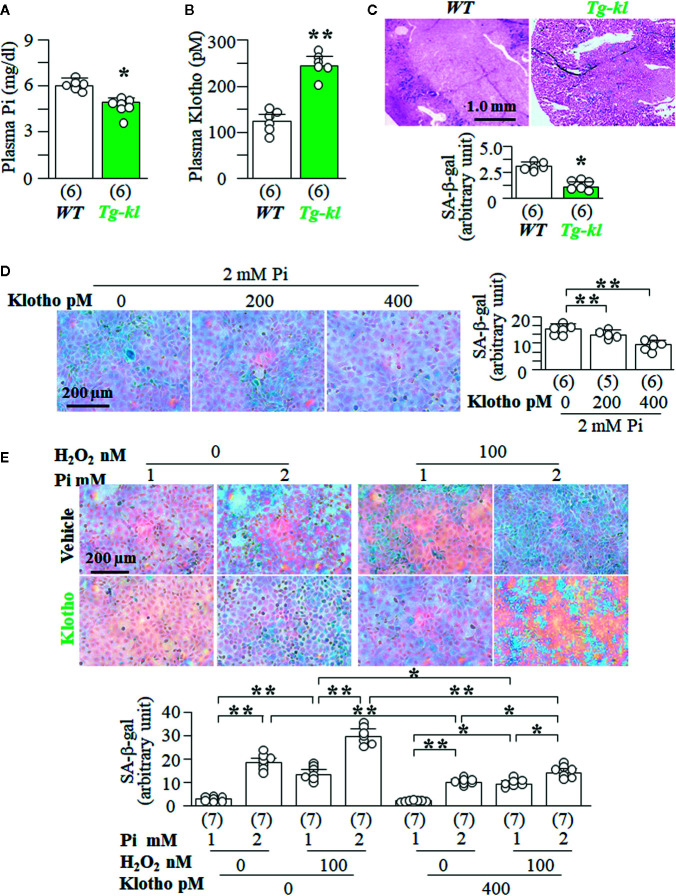
Figure 7.
Klotho inhibits high Pi-induced senescence in vivo and in vitro. (A–C) WT mice and Tg-kl mice were maintained in normal Pi diet and sacrificed at 12 weeks old. Each genotype had 6 mice. (A) Plasma Cr. (B) plasma Klotho. (C) SA-β-gal stain in kidney sections of WT and Tg-kl mice. Upper panel: representative images of SA-β-gal stain; bottom panel: quantitative score of SA-β-gal stain. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. with scatter plots of individual data points. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 between two genotypes by un-paired Student t test for (A–C). (D, E) NRK cells were seeded in 6-well plates and treated 2 mmol/l Pi with Klotho or vehicle (PBS) for 72 h. (D) SA-β-gal stain in NRK cells. Left panel: representative images of SA-β-gal stain; right panel: quantitative score of SA-β-gal stain. Sample number in each group is presented in bracket underneath corresponding bar. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. with scatter plots of individual data points. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 between two groups by one-way ANOVA followed by Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test. (E) SA-β-gal stain in NRK cells treated with different levels of Pi or H2O2 or Klotho or vehicle. Upper panel: representative images of SA-β-gal stain; bottom panel: quantitative score of SA-β-gal stain. Sample number in each group is presented in bracket underneath corresponding bar. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. with scatter plots of individual data points. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 between two groups by three-way ANOVA followed by Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test.