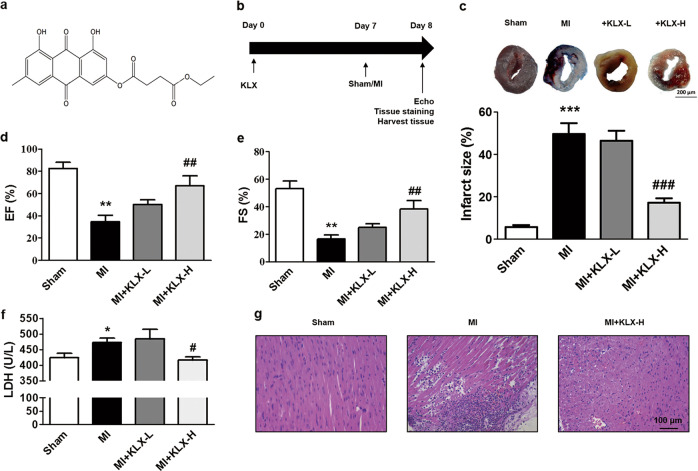
Fig. 1.
Effects of KLX on myocardial injury and cardiac function in post-MI mice. a Chemical structure of KLX (C21H18O8). b The experimental protocol for the preventative KLX study in MI mice. c Representative LV sections stained with TTC and Evans blue (upper panel) and statistical data of the LV infarct size. The infarct size (%) is expressed as the percentage of infarct area relative to the total LV area. The blue area represents the nonischemic region, the area at risk is stained red, and the infarct region is stained white. Scale bar = 200 μm; n = 5. KLX-L: 20 mg ·kg−1; KLX-H: 40 mg· kg−1. d, e Echocardiographic analysis of the LV EF% and FS% in the mice; n = 7–8. f Serum LDH level in the mice; n = 5. g Representative H&E staining of paraffin sections of the LV from the mice (×200). Scale bar = 100 μm. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. sham; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. MI