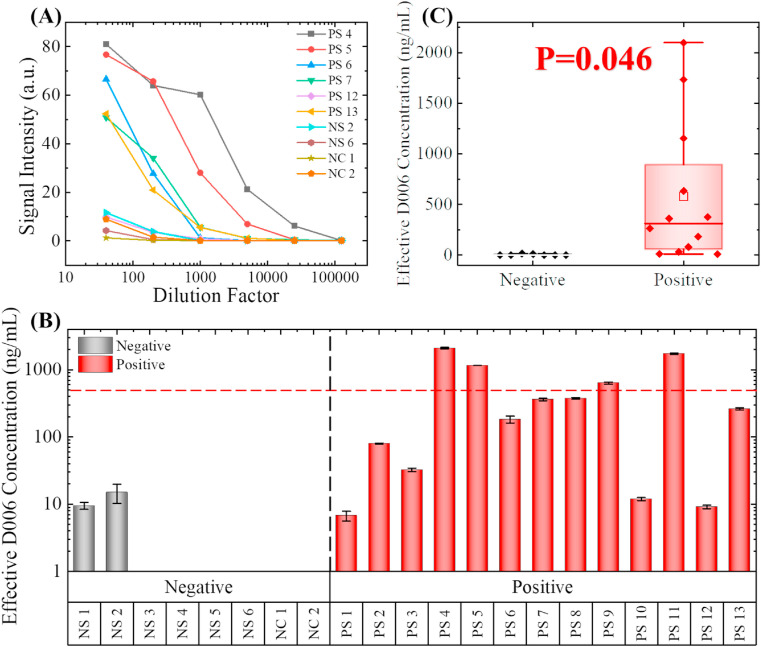
Fig. 4.
Detection of anti-S1 IgG in recovered COVID-19 patients' serum. (A) Serial dilution tests with 10 representative samples, including six positive samples (PS), two negative samples (NS), and two commercially available negative controls (NC). Note that the positive/negative was determined with traditional plate-based ELISA. 200 X dilution in 2.5% BSA was determined to be the optimum dilution factor for differentiating the strong positive samples from the weak positive and negative samples. (B). Effective D006 concentrations for all nineteen samples and the two negative controls. The concentrations are marked as 0 ng/mL if the calculated concentration was below 2 ng/mL (too close to LLOD). The error bars are generated from duplicate measurements. Only four samples have effective D006 concentrations higher than 500 ng/mL after 200 times of dilution. (Note that PS4 and PS11 exceeded the upper limit of detection). (C). Statistical comparison between the negative samples and the positive samples. Since p < 0.05, the difference between these two groups is statistically significant.