Figure 1.
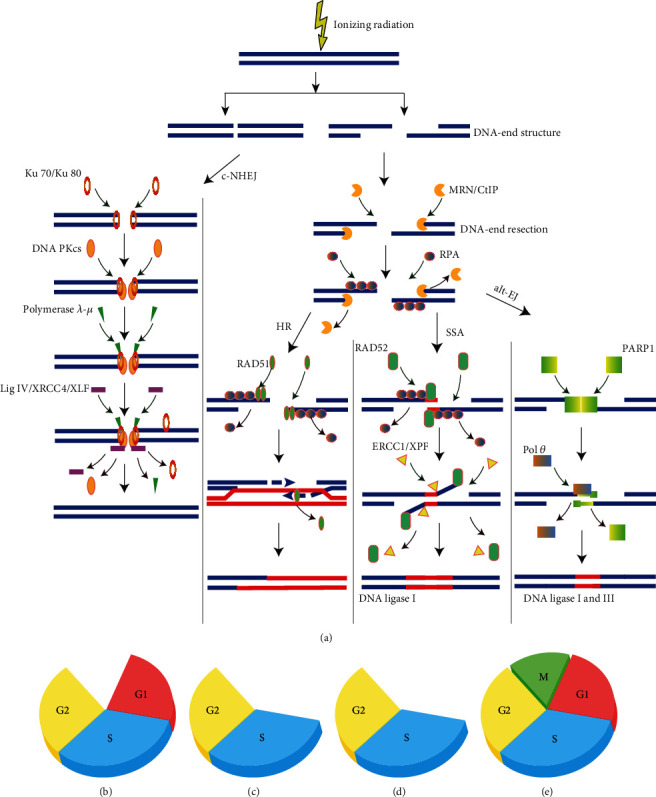
(a) Major repair pathways for DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) generated by ionising radiation (IR). When IR-induced DNA DSBs have blunt double-strand DNA ends or contain short single-strand DNA ends, the classical nonhomologous end joining (c-NHEJ) is initiated by the binding of the Ku70/80 heterodimer followed by the recruitment of DNA-PKcs and polymerase. When DNA resection occurs, the pathways of homologous recombination (HR), alternative end joining (alt-EJ), and single-strand annealing (SSA) can be activated to repair the IR-induced DNA DSBs by the recruitments of different proteins. (b–e) The major repair pathways ((b) c-NHEJ, (c) HR, (d) SSA, and (e) alt-EJ) for processing IR-induced DNA DSBs have a distinct cell-cycle dependence.
