Figure 2.
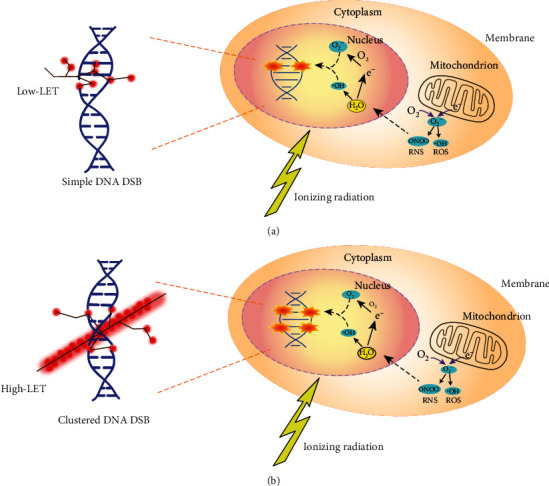
The direct and indirect effects of ionising radiation (IR) in cells. The schematic shows IR can lead to the DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) directly by the induction of radiation energy deposition, or indirectly by the generation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS and RNS). The direct effects are mainly determined by the radiation quality, i.e., low and high linear energy transfer (LET) can generate distinctive patterns of ionisation events on the structures of DNA molecules. When doses are the same, low-LET (a) and high-LET (b) radiation can generate different types and distributions of DNA DSBs. The IR-induced ROS and RNS are not only from the interaction of IR with water and molecules but also as a result of leakage of mitochondrial dysfunctions.
