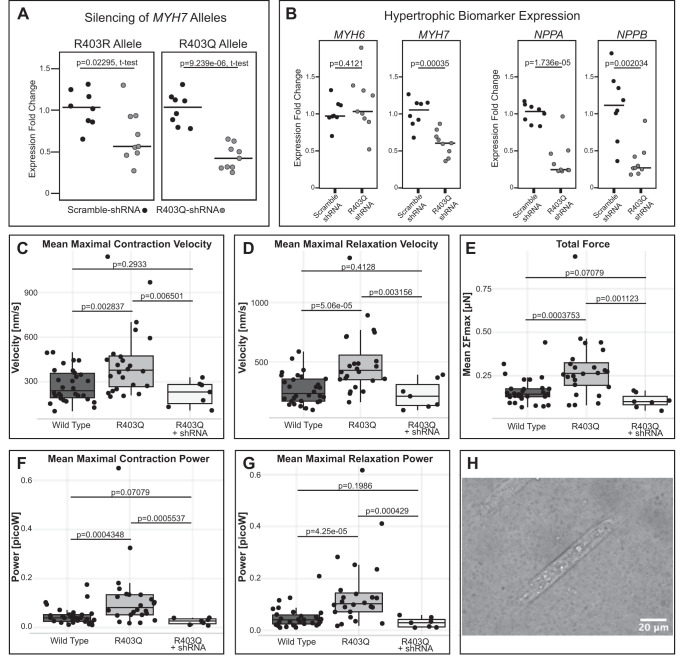
Fig. 2.
shRNA knockdown reduces hypertrophic biomarker expression and contractile disease phenotypes in MYH7-R403Q human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs). A: heterozygous MYH7-R403Q hiPSC-CMs transduced with a virally delivered R403Q-targeting shRNA (H10.8L) show reduced expression of both the R403Q and R403R alleles as compared with hiPSC-CMs transduced with a scrambled shRNA. Individual data points and medians are plotted, expression normalized to scramble-treated RNA expression for either the R403R or R403Q allele individually. hiPSC-CMs were shRNA-treated on day 20 of differentiation, and RNA was collected after 5 days of treatment. B: MYH7-R403Q hiPSC-CMs treated with this same R403Q-targeting shRNA show reduction of overall MYH7 RNA levels, but no change in MYH6 expression levels, as well as a decrease in RNA expression of hypertrophic biomarkers NPPB and NPPA. Individual data points and medians are plotted, expression normalized to scramble-treated RNA expression. All P values are from a two-sided t test. C–G: untreated MYH7-R403Q hiPSC-CMs from a sibling cell line (CDI Line 01178.103) show increased velocity, force, and power during contraction and relaxation compared with wild-type (WT) hiPSC-CMs, as measured by traction force microscopy. Viral transduction with the R403Q-targeting H10.8L shRNA reduces these contractile measures back to wild-type levels. H: example image of a WT hiPSC-CM on a cellular micropatterning device. These Matrigel patterns were printed onto a polyacrylamide gel with embedded fluorescent beads to track contractile motion.