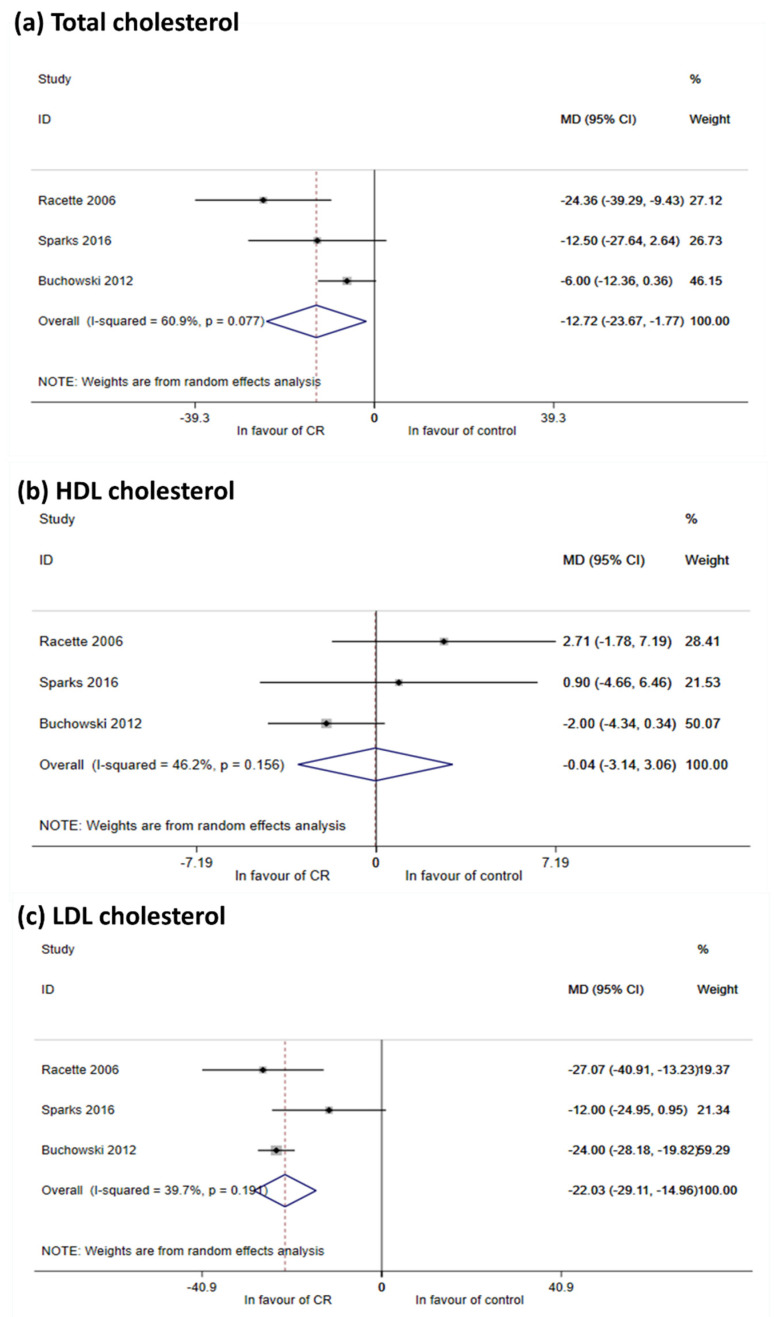
Figure 3.
Meta-analysis for LDL, HDL and total cholesterol. (a) Meta-analysis using random effect method, outcome Total cholesterol. Meta-analysis was performed using post mean value (or median value) or mean change within groups and calculating mean differences (MD, with their 95% CI). Despite the moderate heterogeneity, meta-analysis shows that CR is effective in total cholesterol reduction All MDs are expressed in mg/dL; (b) meta-analysis using random effect method, outcome HDL cholesterol. Meta-analysis was performed using post mean value (or median value) or mean change within groups and calculating mean differences (with their 95% CI). Mean estimate is in favor of control, but non statistically significant. Only Racette 2006 showed an iatrogenic effect of CR. All MDs are expressed in mg/dL; (c) meta-analysis using random effect method, outcome LDL cholesterol. Meta-analysis was performed using post mean value (or median value) or mean change within groups and calculating mean differences (with their 95% CI). Impact on LDL reduction is showed considering all studies together. Heterogeneity is moderate. All MDs are expressed in mg/dL.