Figure 1.
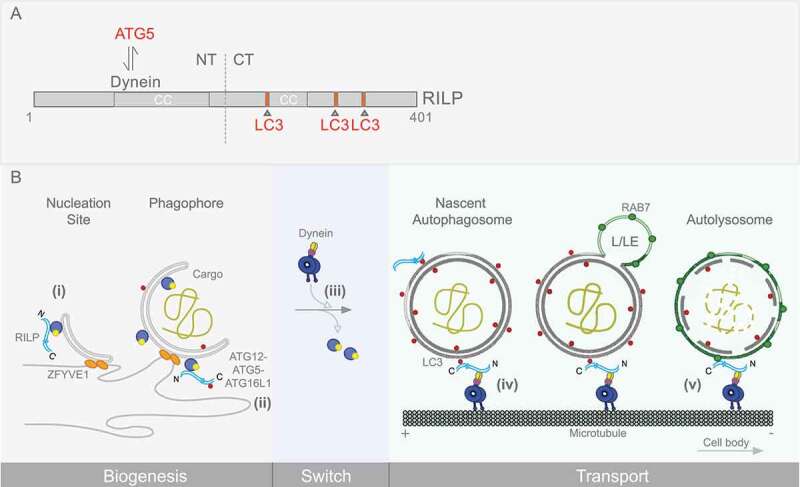
RILP domain organization and sequential roles in the autophagy pathway. (A) RILP domain organization and interactors are shown. The RILP N terminus interacts with cytoplasmic dynein, while the C terminus binds the late endosomal marker, RAB7. Our work also shows RILP to interact with ATG5 on phagophore membranes, and with LC3 on autophagosomes. Three C-terminal LC3-interacting regions (LIRs) were identified, and are depicted. (B) RILP roles at different stages in autophagy progression are shown. Nucleation, expansion of the phagophore membrane and maturation of the autophagosome are depicted. RILP is detected on nascent as well as more fully formed phagophore membranes, associated with ATG5 (i, ii). RILP persists on mature autophagosomes, linked through LC3 (iii, iv). RILP remains associated with AP-LE membranes through LC3 and RAB7 (v), until lysosomal fusion. This pathway is activated by MTOR regulation of RILP expression and distribution, and is required for autophagic clearance.
