Figure 1.
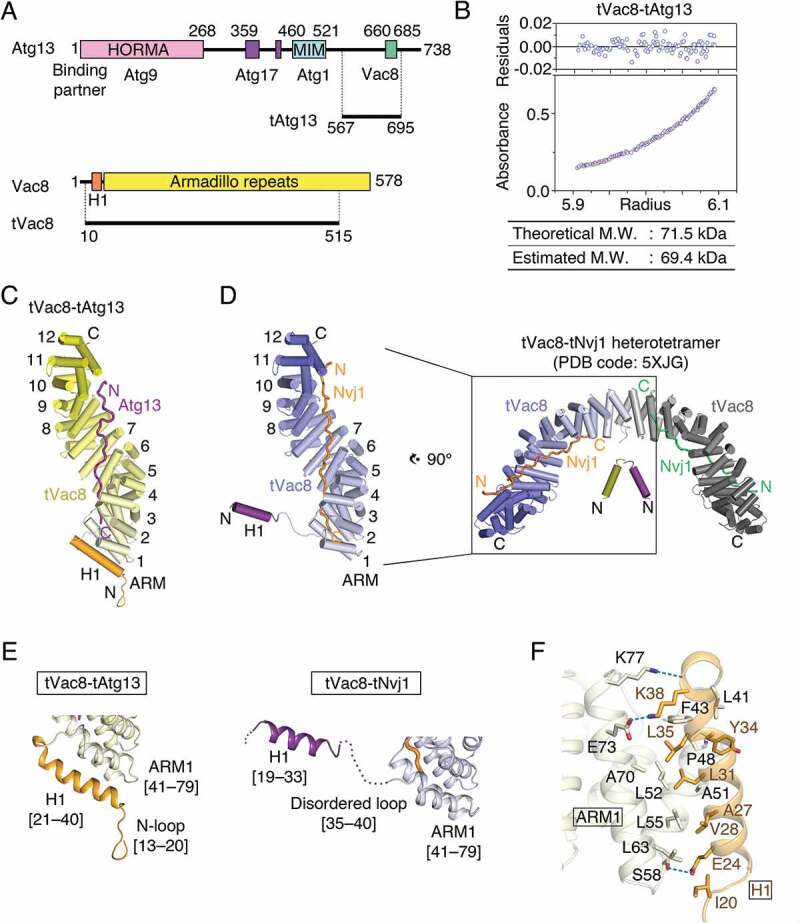
Structure of the tVac8-tAtg13 complex. (A) Domain structures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Atg13 and Vac8. Previously identified conserved domains are marked by colored boxes, and the binding regions of associated proteins are indicated below. Residues 567–695 of Atg13 (designated as tAtg13) and residues 10–515 of Vac8 (designated as tVac8) were used for crystallization and biochemical experiments in this work. HORMA, Hop1, Rev7 and MAD2 domain; MIM, microtubule interacting and transport (MIT)-interacting motif. (B) Analytical ultracentrifugation (AUC) analysis of the molecular weight (M.W.) of the tVac8-tAtg13 complex in solution. The bottom panel indicates a representative plot of absorbance profiles of 2.5 μM tVac8-tAtg13 following a centrifugation run at 13,604 × g for 16 h at 20°C, and the top panel presents the residuals between the experimental data and the fitted line. (C) Overall structure of tAtg13 (purple) bound to the armadillo (ARM) repeat core of Vac8 (yellow). The structure was determined by molecular replacement using tVac8 as a search model (PDB code: 5XJG) and refined to 2.9 Å resolution (Table S2). The H1 regulatory helix of Vac8 is highlighted in orange (see the main text for an explanation of the role of the H1 helix). (D) Comparison of the overall structures of tVac8-tAtg13 in (C) and tVac8-tNvj1, and the structure of the tVac8 (blue)-tNvj1 (orange) complex displayed in the same orientation as in (C). A previous study revealed that the tVac8-tNvj1 complex forms a heterotetramer as shown on the right [24], while the tVac8-tAtg13 complex in (C) forms a heterodimer. The arrangement of the H1 helix in the tVac8-tNvj1 complex is emphasized as a purple cylinder. (E) Cartoon representation comparing the conformation of the H1 helices of tVac8-tAtg13 and tVac8-tNvj1 complexes. In the tVac8-tAtg13 structure (left), the H1 helix (orange) is composed of residues 21–40, and is directly associated with 2 helices of the first ARM (ARM1). By contrast, the H1 helix in the tVac8-tNvj1 complex (right, purple) consists of residues 19–33, which point away from ARM1 via a disordered loop comprising residues 35–40 (dotted line). (F) Cartoon representation showing the interactions between the H1 helix (orange) and ARM1 (pale yellow) of tVac8 in the structure of the tVac8-tAtg13 complex. Residues involved in the interaction are shown in ball-and-stick representation. Oxygen and nitrogen atoms are colored red and blue, respectively, and blue dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
