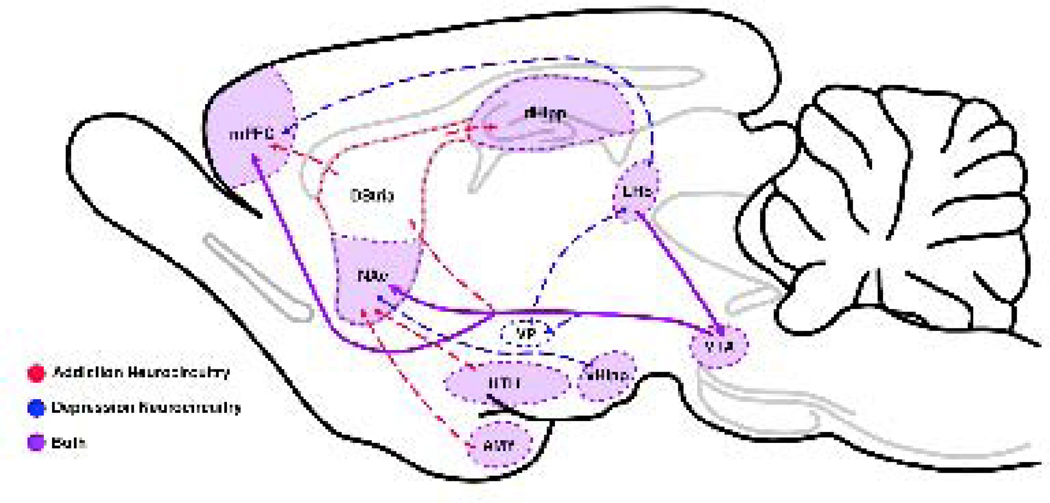
Figure 2.
Involvement of overlapping neurocircuitry in both addiction and depression. Neural changes occuring along the mesolimbic dopaminergic reward pathway in drug addiction strongly overlap with those occurring within the same areas in depression. In both addiction and depression changes occur within the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), nucleus accumbens (NAc), dorsal hippocampus (DHipp), ventral hippocampus (VHipp), hypothalamus (HTH), Lateral Habenula (LHb), and amygdala (AMY). Neural changes induced by ketamine mimic those induced by other drugs of abuse.