Figure 6.
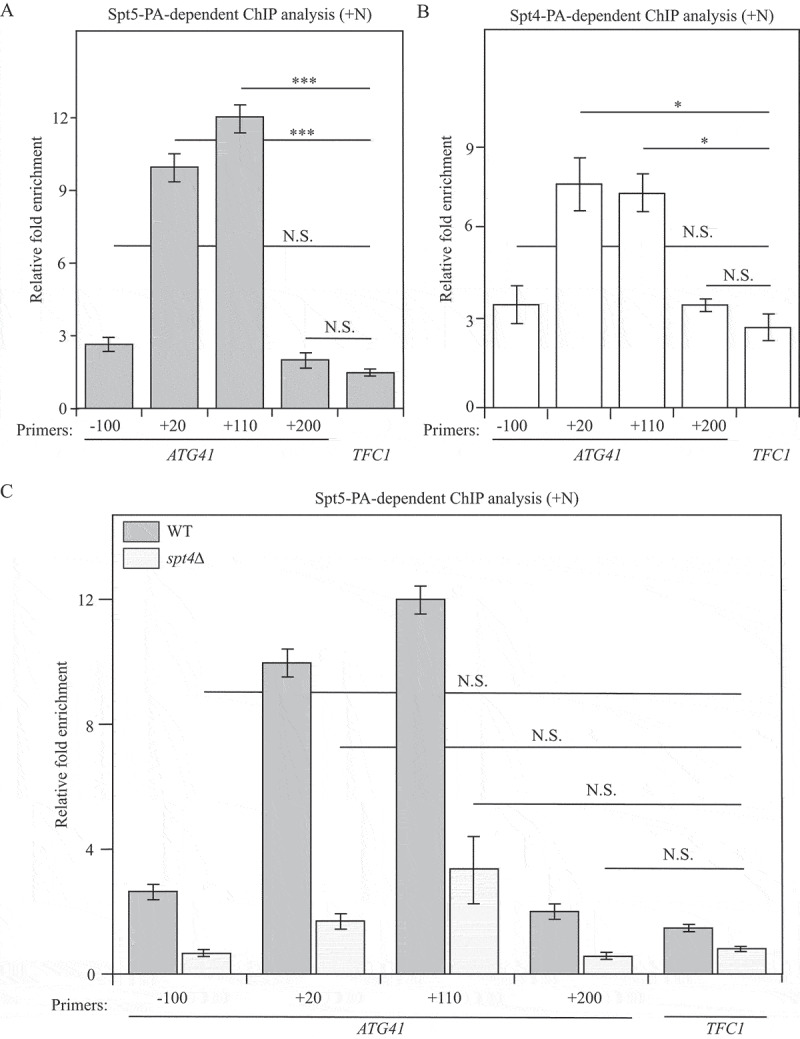
Spt5 binds to ATG41 DNA in an Spt4-dependent manner. (A-C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) was done in Spt5-PA (WXY102), Spt4-PA (WXY106) and spt4∆ Spt5-PA (WXY103) strains. The ChIP samples were collected in the growing condition (mid-log phase). RT-qPCR was used for quantitative analysis. The primers for ChIP cover different DNA regions from the promoters through the ORF in ATG41. “-” indicates upstream of the ATG start codon, and “+” indicates downstream of the ATG start codon. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of ChIP samples of the Spt5-PA (WXY102) strain. The values were normalized to the input. The error bars show the SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. p values in each region are reported for the comparison with the negative control, TFC1. ***, p < 0.005; N.S., not significant. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of ChIP samples of the Spt4-PA (WXY106) strain. The error bars show the SEM of at least 3 independent experiments: *, p < 0.05; N.S., not significant. (C) RT-qPCR analysis of ChIP samples of Spt5-PA (WXY102) and spt4∆ Spt5-PA (WXY103) cells. The values were normalized to the input DNA. TFC1 was used as a negative control and the error bars represent the SEM of at least 3 independent experiments. The significance analysis for spt4∆ strains was noted: N.S., not significant.
