Figure 7.
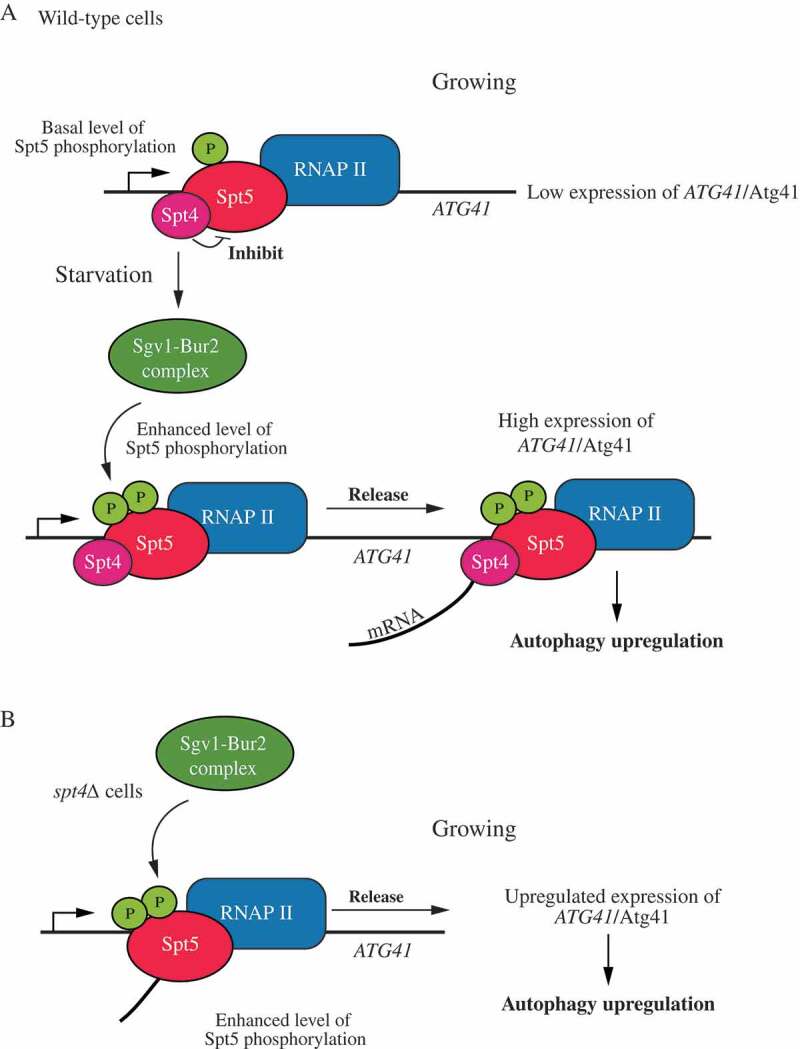
A model for Spt4-Spt5-dependent regulation of ATG41. (A) In wild-type cells under growing conditions, the Spt4-Spt5 complex may inhibit transcription of ATG41 through an Spt4-dependent interference with Spt5 phosphorylation, causing the complex to accumulate near the TSS. After starvation, phosphorylation of Spt5 by the Sgv1-Bur2 kinase complex releases the inhibitory effect of Spt4 on ATG41 transcription, and the Spt4-Spt5 complex participates in transcription elongation. (B) In spt4∆ cells, Spt5 does not accumulate near the TSS of ATG41, and transcription actively proceeds. Spt5 can also be more efficiently phosphorylated upon the deletion of SPT4.
