Figure 1.
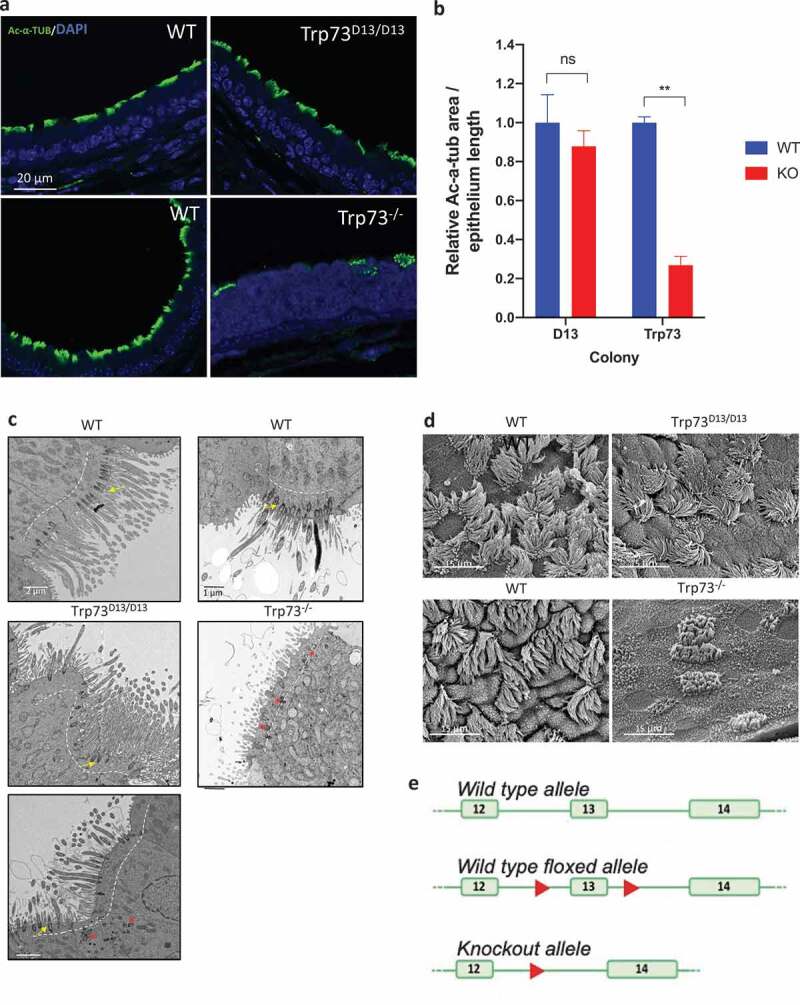
Airway ciliogenesis is preserved in the absence of p73α in Trp73Δ13/Δ13 mice. (a) Representative immunofluorescence images of Ac-α-tub expression (green) in tracheal epithelial cells of Trp73Δ13/Δ13 (top), p73 KO (bottom) mice and the corresponding wild-type shown adjacent. Nuclei were labeled with DAPI (blue). (b) Quantification of Ac-α-tub IF signal area normalized to the length of epithelia (Δ13 colony; WT & KO (Trp73Δ13/Δ13) n = 3 images from 3 mice. Trp73 colony; WT n = 3 images from 2 mice, p73 KO n = 3 images from 2 mice). (c) Representative TEM photomicrographs of tracheal epithelial cells in Trp73Δ13/Δ13 (left) and p73 KO (right) mice and the corresponding wild-type shown above. Dotted lines indicate the apical surface. Basal bodies were correctly docked at the surface of WT and most Trp73Δ13/Δ13 cells (yellow arrows) and aberrantly located in Trp73Δ13/Δ13, as in the p73 KO (red asterisks). (d) Representative SEM images of Trp73Δ13/Δ13 and p73 KO mice. Adjacent is the corresponding wild-type. All data are presented as mean values relative to WT ± SEM and ** = P < 0.01, ns = not significant. (e) Schematic representation of the targeting strategy employed to generate the Trp73Δ13/Δ13 mice. Deletion of exon 13 results in generation of an ectopic splicing junction exon 12–14, which results in p73beta. The diagram is readapted from Amelio et al, PNAS 2020.
