FIGURE 6.
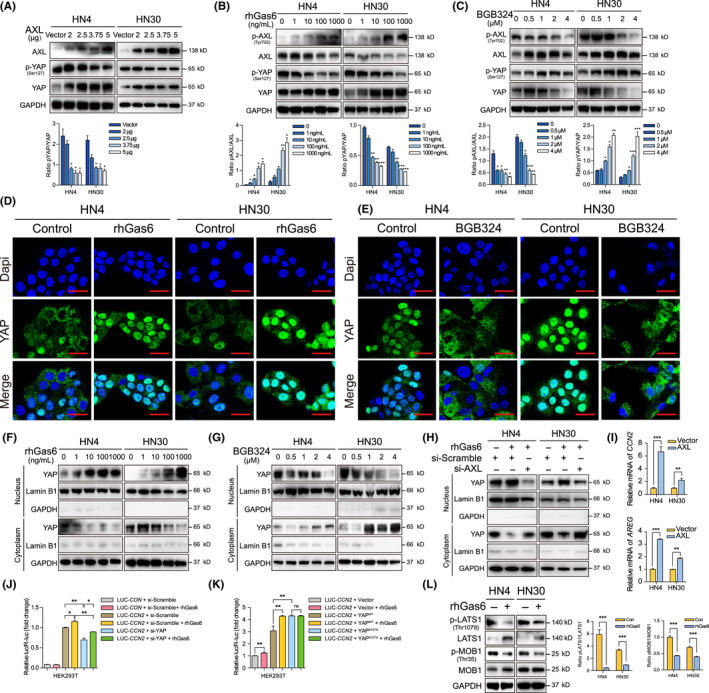
AXL promotes Yes‐associated protein (YAP) nuclear translocation and transcriptional regulation via dephosphorylation. A, P‐YAP was detected after AXL plasmid transfection for 48 h. B, P‐YAP was detected after treatment with 2% FBS for 12 h and rhGas6 for 1 h. C, After AXL inhibitor BGB324 treatment for 24 h, p‐YAP expression was assessed. D, Cells were treated with 2% FBS for 12 h and 1000 ng/mL rhGas6 for 1 h. Confocal immunofluorescence assay was used to visualize YAP localization. Scale bars: 20 μm. E, The localization of YAP was assessed after treatment with 2 μmol/L BGB324 for 24 h. Scale bar: 20 μm. F, Nuclear and cytoplasmic YAP proteins were separated and analyzed after treatment with 2% FBS for 12 h and 1000 ng/mL rhGas6 for 1 h. G, YAP expression in nucleus and cytoplasm were analyzed after 2 μmol/L BGB324 treatment for 24 h. H, Nuclear and cytoplasmic YAP were determined after si‐AXL transfection with 2% FBS for 48 h and 1000 ng/mL rhGas6 treatment for 1 h. I, CCN2 and AREG relative mRNA expression was measured after AXL plasmid transfection for 24 h. J, CCN2‐promoter activities were detected after cotransfection of si‐YAP with 2% FBS for 24 h and 1000 ng/mL rhGas6 treatment for 1 h. K, CCN2‐promoter activities were analyzed after cotransfection of YAPWT or YAPS127A plasmid with 2% FBS for 24 h and 1000 ng/mL rhGas6 treatment for 1 h. L, P‐LATS1 and p‐MOB1 were determined after treatment with 2% FBS for 12 h and 1000 ng/mL rhGas6 for 1 h. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, according to Student t test
