Figure 4.
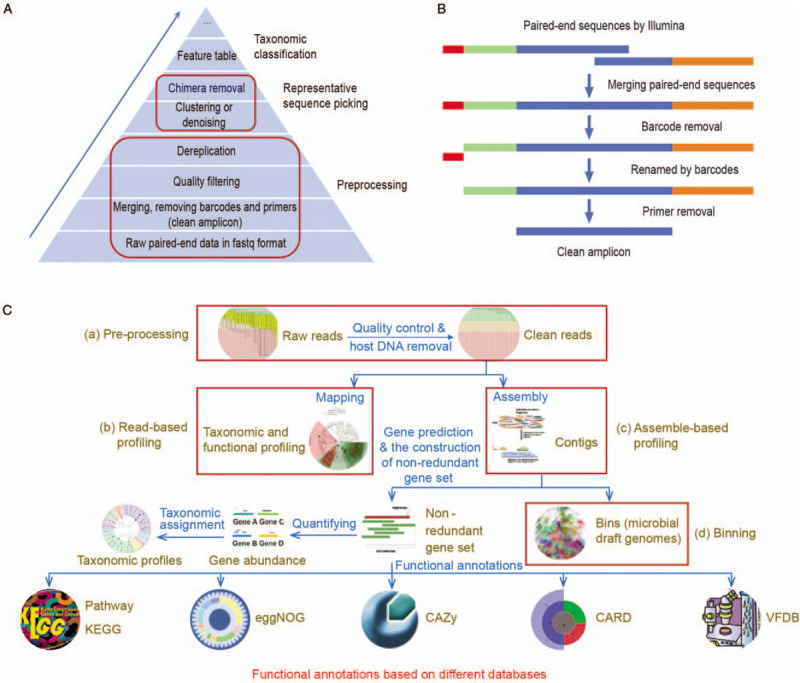
Bioinformatics analysis pipelines for human microbiome research. (A) Main steps for taxonomic profiling of amplicon data. (B) Typical flowchart of pre-processing in amplicon data: from raw paired-end sequences to clean amplicons. (C) Analysis pipeline for metagenomic sequencing data. (a) Pre-processing. It involves removing low-quality, adaptor and host reads. The output corresponds to clean reads. (b) Read-based profiling. It involves that reads map against the databases to infer taxonomic and metabolic profiles. (c) Assemble-based profiling. It involves assembling short reads into contigs, predicting genes, constructing non-redundancy gene catalog, and blasting against the databases to profile taxonomy and functions. (d) Binning. It involves recovering draft genome of uncultured microbe and reconstruction of phylogenetic and metabolic pathways. CARD: Comprehensive antibiotic resistance database; CAZy: Carbohydrate-active enzymes database; eggNOG: Evolutionary genealogy of genes: non-supervised orthologous groups; KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes; VFDB: Virulence factor database.
