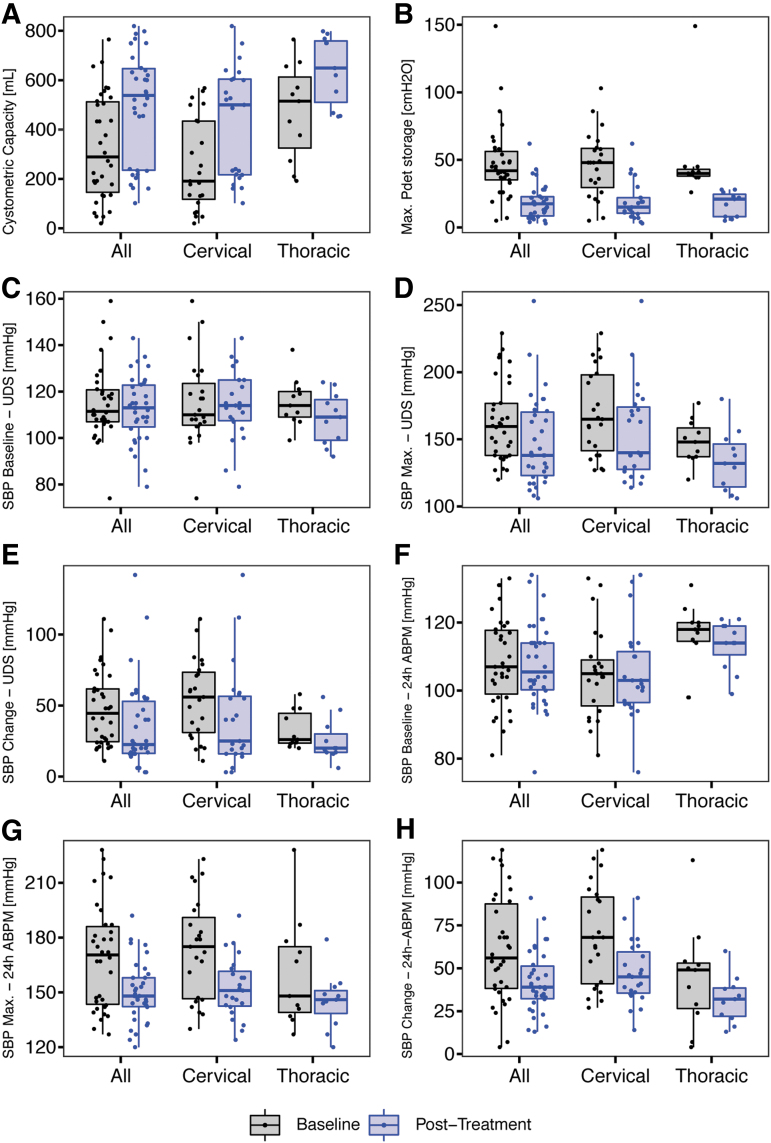
FIG. 1.
Pre/post-treatment comparisons of lower urinary tract function, cardiovascular changes during urodynamics (UDS) and in daily life, and quality of life related to autonomic dysreflexia (AD) symptoms and incontinence across all participants and injury-level–dependent subgroups. Compared with the initial assessment, we observed a variety of changes post-treatment: (A) cystometric capacity, (B) maximum detrusor pressure, (C) baseline systolic blood pressure (SBP) at the beginning of UDS, (D) maximum SBP during UDS, (E) severity of AD during UDS (i.e., maximum change in SBP), (F) baseline SBP in daily life (i.e., 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring [24-h ABPM]),(G) maximum SBP in daily life, and (H) severity of AD in daily life (i.e., maximum change in SBP observed during 24-h ABPM). Data are presented at group level using box plots (median, interquartile range) and individually (dots).