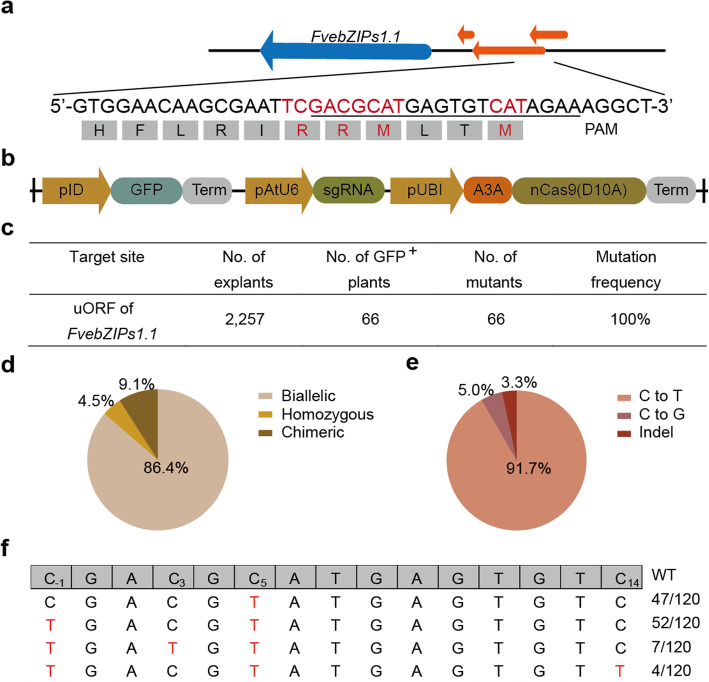
Fig. 2.
Engineering the SC-uORF of FvebZIPs1.1 using A3A-PBE. a Diagram of the uORFs in FvebZIPs1.1 and the target of A3A-PBE. Part of the amino acid sequence of the SC-uORF and the corresponding codons in the DNA sequence are shown, and the targeted sequence is underlined. The two ATGs and two codons that encode conserved amino acids (RR) of SC-uORF are marked in red. b Schematic of the A3A-PBE vector. GFP fluorescence was used to identify transgenic plants. pUbi, maize Ubiquitin-1 (Ubi-1) gene promoter. pID, root loci promoter. c Frequencies of mutations induced by A3A-PBE in T0 strawberry plants. GFP+, GFP fluorescence positive. d Proportions of the different types of mutation in T0 strawberry plants. e Proportions of C-to-T changes, C-to-G changes, and indels induced by A3A-PBE at the target site. f The four different alleles (single and multiple C-to-T conversions) of the uORF among the T0 mutant plants, and their frequencies. Nucleotide substitutions are indicated in red. The letter subscripts on the cytosines in the WT sequence indicate the positions of these bases in the protospacer, counting from the distal end to the protospacer-adjacent motif. Frequency: number of a given allele /total numbers of alleles