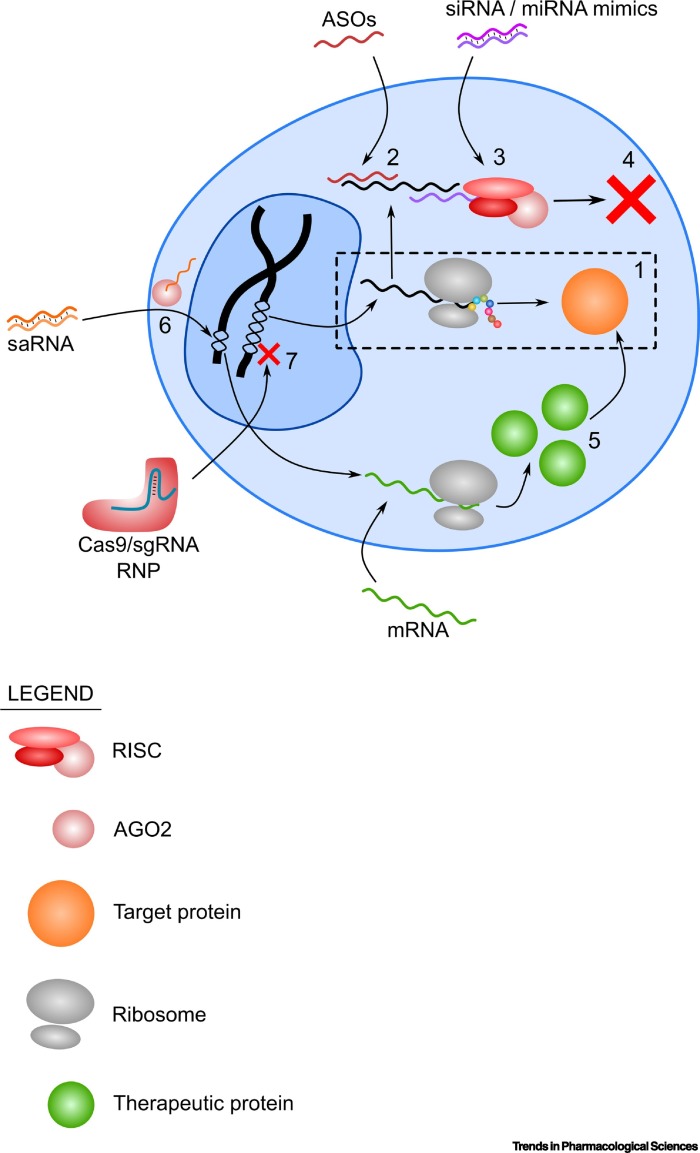
Figure 1.
Overview of Different Mechanisms of Action of Different RNA Therapeutics.
(1) Without therapeutic RNA molecules, the translation of a pathogenic protein proceeds without inhibition (shown in the broken line box). (2) ASOs hybridize to the target mRNA, while the (3) siRNA/miRNA mimics utilize the RISC in the RNAi pathway to (4) inhibit translation of target mRNA. (5) Overexpression of a therapeutic protein that counteracts the function of the pathogenic protein can be done by delivering the mRNA of the therapeutic protein. (6) saRNA can be delivered to the cell where it binds to AGO2, is imported to the nucleus, and in turn activates an endogenous gene. (7) A more permanent approach to remove the pathogenic protein is by gene knockout using Cas9 and sgRNA RNPs. Abbreviations: AGO2, argonaute 2; ASO, antisense oligonucleotide; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex; RNP, ribonucleoprotein; saRNA, small activating RNA.