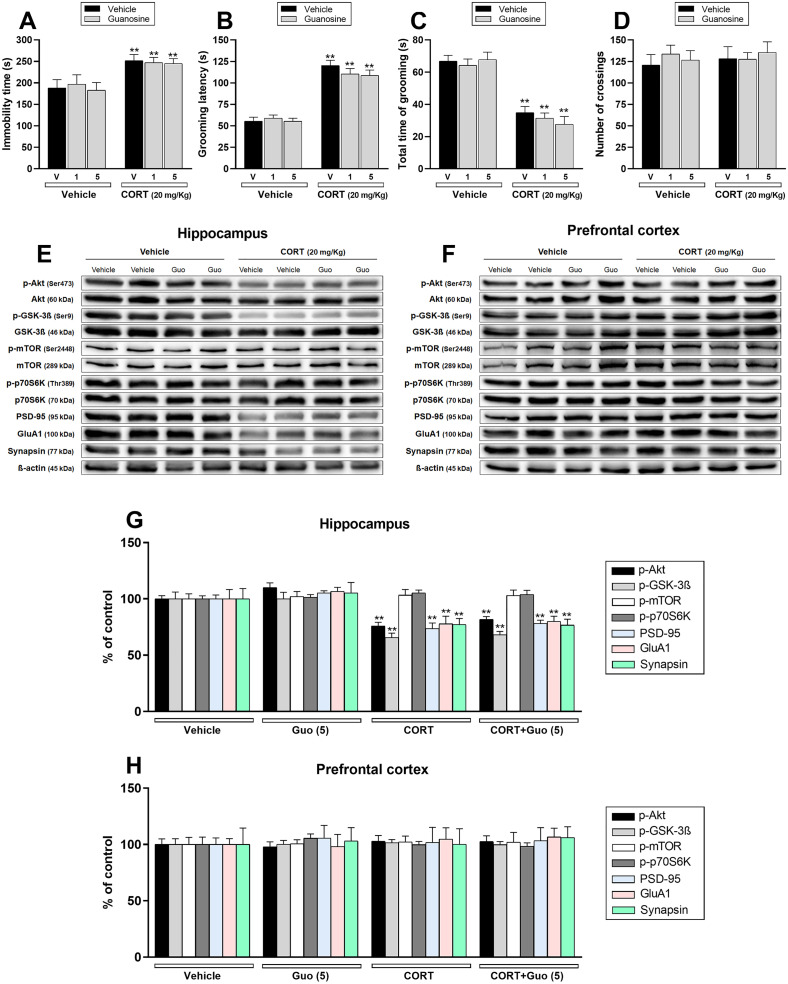
Fig. 4.
Effect of a single administration with guanosine (Guo – 1 or 5 mg/kg, i.p.) 1 week prior to the administration with vehicle or corticosterone (CORT – 20 mg/kg, p.o.) on depression-related behaviors and synaptic markers in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of mice. a Guanosine (1 or 5 mg/kg, p.o) administration did not prevent CORT-induced increase in the immobility time in the TST (n = 8). b, c Guanosine (1 or 5 mg/kg, p.o) administration did not prevent the increase in the grooming latency and reduction in the total time of grooming induced by CORT in the SPT (n = 8). d All groups of mice had comparable number of crossings in the OFT (n = 8). e, f Representative bands of phospho-Akt (Ser473), Akt, phospho-GSK-3β (Ser9), GSK-3β, phospho-mTOR (Ser2448), mTOR, phospho-p70S6K (Thr389), p70S6K, PSD-95, GluA1, synapsin, and β-actin in the (e) hippocampus and (f) prefrontal cortex of mice. g, h Quantification of these proteins in the (g) hippocampus and (h) prefrontal cortex. Values are expressed as means ± S.E.M (n = 7). ** p < .01 as compared with the vehicle-treated group (two-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls post hoc test).