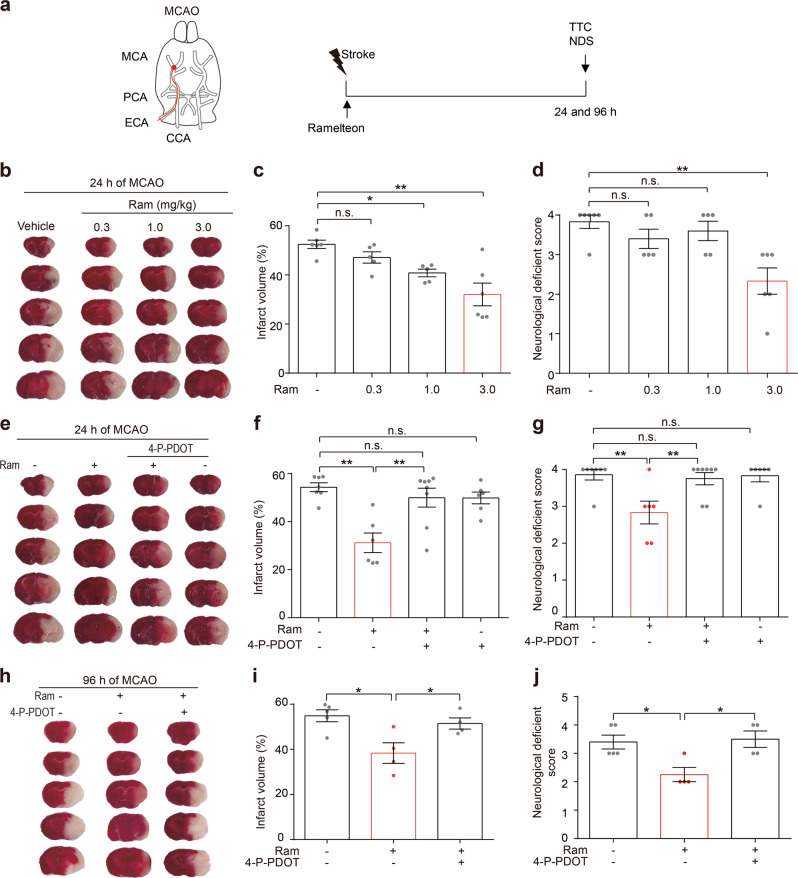
Fig. 1.
Ramelteon protected against middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)-induced acute ischemic brain injury. a Experimental design of acute ischemia is shown. b Ramelteon at 0.3, 1.0 or 3.0 mg/kg was administered orally at the onset of MCAO. Representative brain slices are shown after TTC staining. c The infarct volumes and d neurological deficit scores were accessed at 24 h after MCAO. e Mice were treated with ramelteon at 3.0 mg/kg, 4-P-PDOT at 3.0 mg/kg or cotreatment after surgery. 4-P-PDOT was injected 0.5 h before ramelteon administration. n = 5 to 8 for each group. f The brain infarct volumes and g neurological deficit scores were measured as mentioned previously. h, i The brain infarct volumes and j neurological deficit scores were measured after 96 h. n = 4 to 5 for each group. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM. Statistical comparisons were performed with a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; n.s. (not significant) vs the indicated group