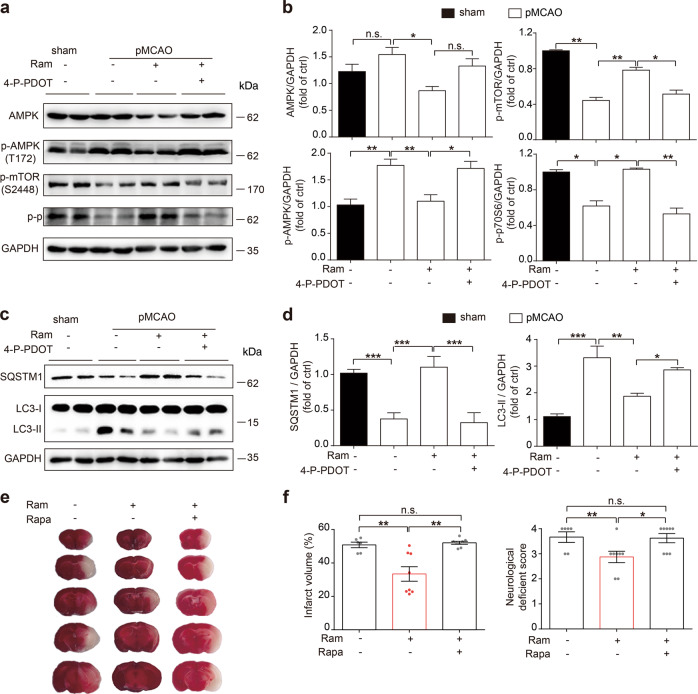
Fig. 4.
Ramelteon activated the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway and inhibited autophagy in acute ischemic brain injury. a Mice were administered ramelteon at 3.0 mg/kg or were cotreated with 4-P-PDOT at 3.0 mg/kg after MCAO. The expression of AMPK, p-AMPK (T172), p-mTOR (S2448), p-p70S6 and GAPDH in the ischemic penumbra was measured by Western blot analysis 24 h after MCAO. n = 4 for each group. b Semiquantitative analyses of AMPK, p-AMPK (T172), p-mTOR (S2448), and p-p70S6 are shown. c The expression of SQSTM1 and LC3B was determined by Western blot analysis. d Semiquantitative analyses of SQSTM1 and LC3-II are shown. e Mice were treated with ramelteon at 3.0 mg/kg or were cotreated with rapamycin at 10.0 μmol at the onset of ischemia. Rapamycin was dissolved in saline and intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.) injected. f Infarct volumes and NDS were accessed as previously described. n = 8-10. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. Statistical comparisons were performed with a one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; n.s. (not significant) vs the indicated group