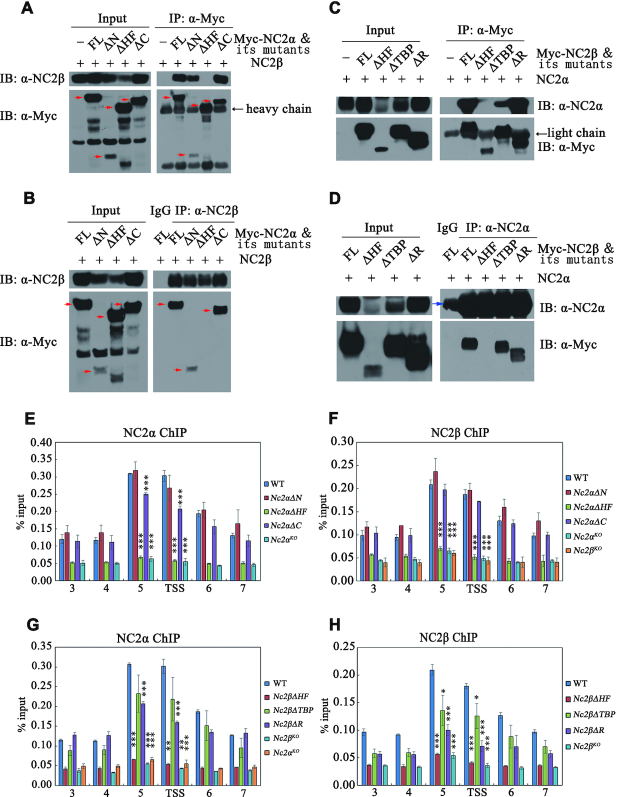
Figure 5.
HF domains in NC2 subunits are essential for its integrity and ability to bind at cat-3 locus. (A, B) Mapping of the NC2α region responsible for the interaction with NC2β in Nc2αKO strain with ectopically expressing wild-type Myc-NC2α or its various deletion mutants. Immunoprecipitation assays with anti-Myc antibody (A) or anti-NC2β antibody (B), the eluates were detected by western blot analysis using anti-Myc (α-Myc) and anti-NC2β (α-NC2β) antibodies. The red arrows denote specific bands, and the black arrow shows heavy chain. (C, D) Mapping of the NC2β region responsible for the interaction with NC2α in Nc2βKO strain with ectopically expressing Myc-NC2β or its various deletion mutants. Immunoprecipitation assays with anti-Myc antibody (C) or anti-NC2α antibody (D), the eluates were detected by western blot analysis using anti-Myc (α-Myc) and anti-NC2α (α-NC2α) antibodies. The blue arrow denotes heavy chain of IgG, the black arrow shows light chain. (E, F) ChIP assays showing the binding levels of NC2α (E) and NC2β (F) at cat-3 locus in different deletion strains across NC2α coding region at endogenous locus. (G, H) ChIP assays showing the binding levels of NC2α (G) and NC2β (H) at cat-3 locus in different deletion strains across NC2β coding region at endogenous locus. Error bars show s.d. (n = 3). Significance was assessed by using a two-tailed t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 vs. WT.