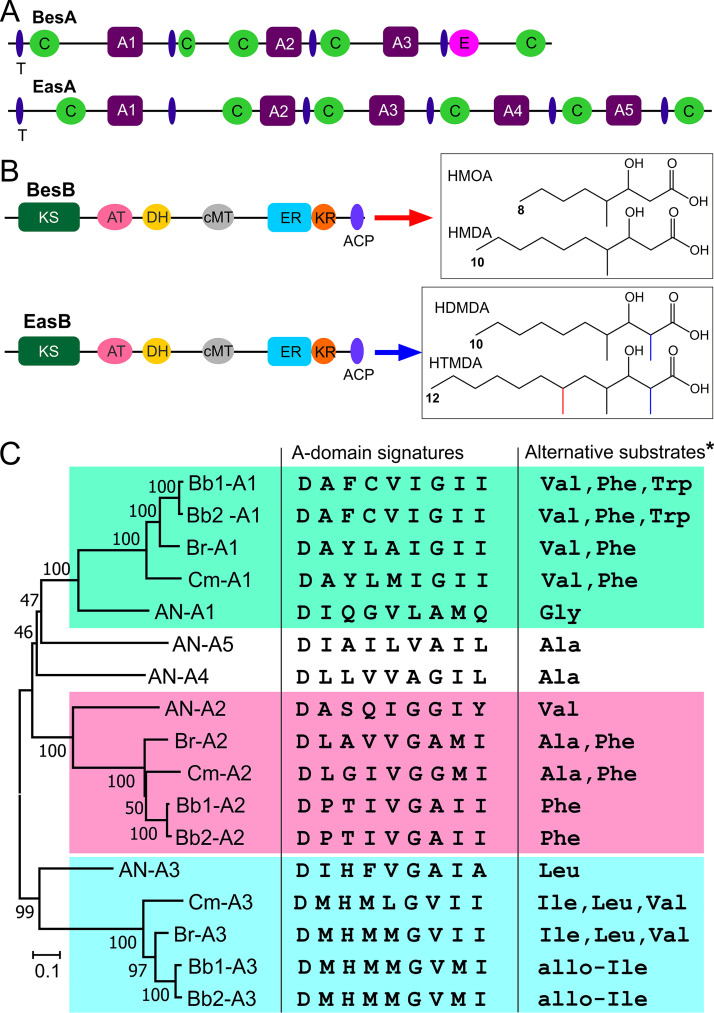
FIG 2.
Conservation and phylogenetic analysis of the core biosynthetic enzymes. (A) Schematic structure comparison between the NRPS enzymes BesA and EasA. Different domains are as follows: C, condensation; A, adenylation; E, epimerization; T, thiolation. (B) Schematic structure comparison between the PKS enzymes BesB and EasB. Different domains are as follows: KS, ketosynthase; AT, acyl transferase; DH, dehydratase; cMT, C-methyltransferase; ER, enoyl reductase; KR, ketoreductase; ACP, acyl carrier protein. Fatty acids are as follows: HMDA, 3-hydroxy-4-methyldecanoic acid; HMOA, 3-hydroxy-4-methyloctanoic acid; HDMDA, 3-hydroxy-2,4-dimethyldecanoic acid; and HTMDA, 3-hydroxy-2,4,6-trimethyldodecanoic acid. (C) Phylogenetic, signature, and alternative substrate analysis of the NRPS A domains from different fungi. *, alternative substrates for the A1 and A2 domains are l-type amino acids, whereas the d-type amino acids are for the A3 domain. Fungal species or strains are as follows: Bb1, B. bassiana strain ARSEF 2860; Bb2, B. bassiana ARSEF 8028; Br, B. brongniartii; Cm, C. militaris; AN, A. nidulans.