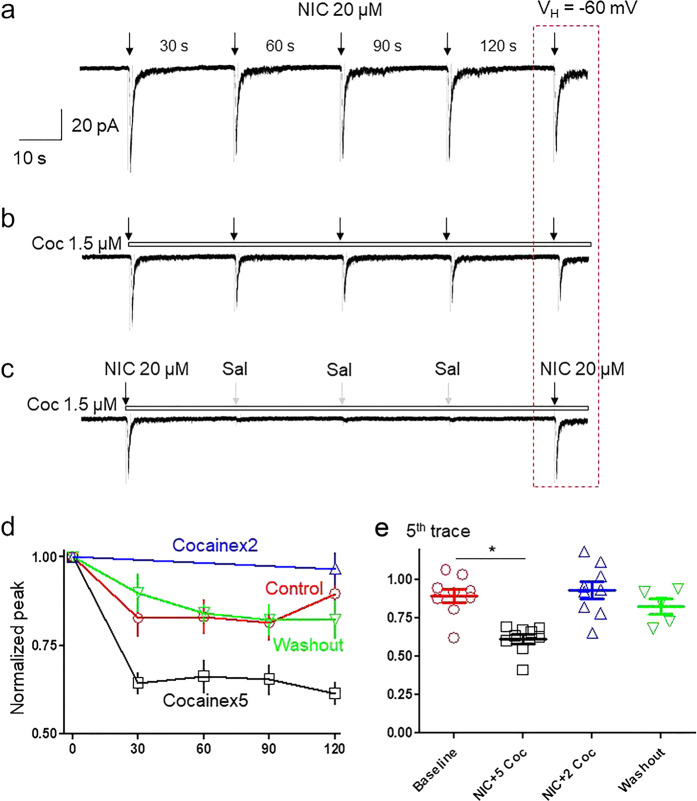
Fig. 4.
Cocaine use-dependently inhibits nicotine response. SH-SY5Y α3β4 nAChRs cell responses when repeatedly exposed to 20 µM nicotine with 1 s exposure at 30 s intervals, indicated by black down arrows (a); when 20 µM nicotine was applied in the presence of 1.5 µM cocaine, indicated by an open horizontal bar (b); or when nicotine and 1.5 µM cocaine were applied for 1 s only at the first and fifth traces, where the gray down arrows indicate application of standard extracellular solution (c). d Line graph comparing the effects of cocaine during five applications of nicotine alone (red line), five applications of nicotine plus cocaine (black line), and two applications of nicotine plus cocaine (blue line). e Bar graph (n = 8) comparing the ratio of the fifth trace to the first trace during repetitive exposure to nicotine alone, nicotine plus five applications cocaine or nicotine plus two applications of cocaine (the first and fifth exposures were nicotine plus cocaine). *P < 0.05 for the difference in effects assessed under the two different nicotine challenge protocols