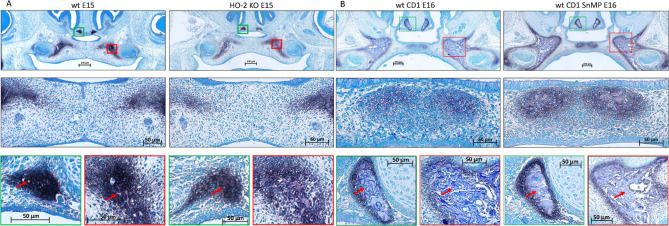
FIGURE 5.
Palatal osteogenesis during MES disintegration: (A) Upper panel: Histochemical stained coronal palatal section for ALP-activity, representative for the wt E15 and HO-2 KO E15 fetuses. Middle panel: Magnification of the central part of the fusing palate including the MES. The palatal mesenchymal cells demonstrated positive staining for ALP-activity. Green panel: Magnification of the nasal septum. A cluster of ALP-activity positive-stained mesenchymal cells was found in the region lateral from the nasal septum including some small bone matrix depositions (red arrow). Red panel: Magnification of the lateral part of the palatal shelve. A cluster of ALP-positive stained mesenchymal cells was found including small bone matrix depositions (red arrow). (B) Upper panel: Histochemical stained sections through the maxilla for ALP-activity, representative for the wt CD1 E16 and wt CD1 SnMP E16 fetuses. Middle panel: Magnification of the central part of the fusing palate. A cluster of ALP-positive stained mesenchymal cells including bone matrix depositions was found at the former location of the MES and was regarded as an osteogenic center. Green panel: Magnification of the nasal septum. A cluster of ALP-positive-stained mesenchymal cells surrounding a large area of bone matrix deposition (red arrow) was found. Red panel: Magnification of the lateral part of the palatal shelve. A cluster of ALP-positive-stained mesenchymal cells in the lateral part of the fusing palate surrounding a large area of bone matrix deposition (red arrow) was found.