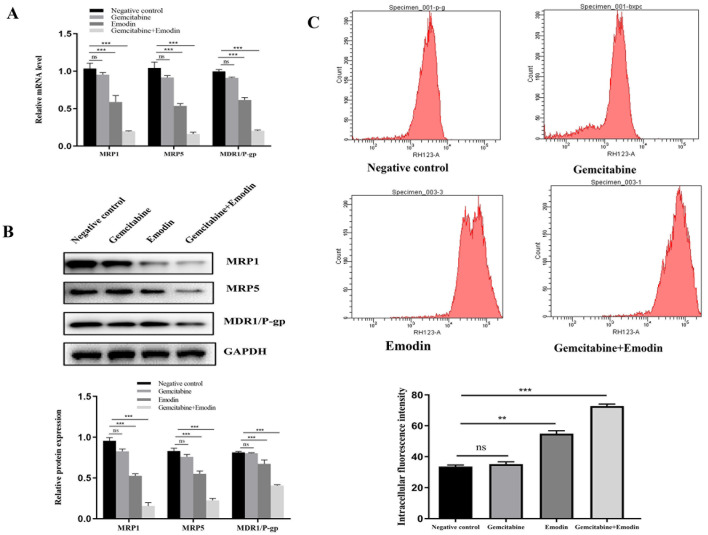
Figure 2.
Detection of p-glycoprotein and efflux function. (A) mRNA expression of MRP1, MRP5 and MDR1-P-glycoprotein examined by reverse transcription quantitative-PCR. Compared with the negative control group, emodin and emodin+gemcitabine treatment all reduced the expression of MDR1/P-glycoprotein and MRP1 and MRP5 in tumor tissues. (B) Expression of MRP1, MRP5 and MDR1-P-glycoprotein determined by western blotting. Compared with the negative control group, emodin and emodin combined with gemcitabine treatment reduced the expression of MDR1/P-glycoprotein and MRP1 and MRP5 in tumor tissues. (C) P-glycoprotein function was investigated in the 4 groups and evaluated using Rho123 staining. Compared with the negative control group, emodin and emodin combined with gemcitabine all increased intracellular fluorescence of Rhodamine 123 intensity in tumor cells. Emodin alone and emodin+gemcitabine treatment reduced the efflux of drug-resistant tumor cells Rho123. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ns, no significance. MDR, multidrug resistance; MRPs, multidrug resistance-related proteins; MRP1, multidrug resistance-related protein 1; MRP5, multidrug resistance-related protein 5.