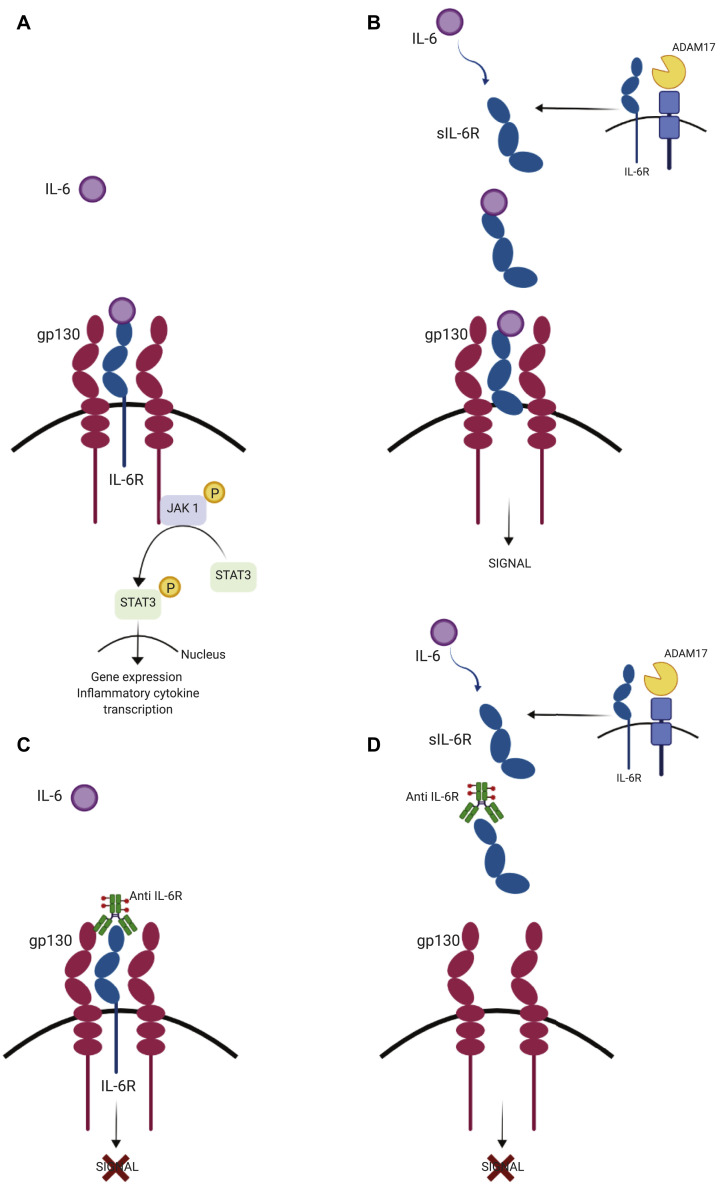
Fig 3.
Classic and trans-signaling IL-6R. A and B, Different signaling pathways stimulated by IL-6. Binding of IL-6 to the membrane-bound or soluble IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) leads to gp130 dimerization and JAK 1–STAT 3 signaling and activation, leading to gene expression of inflammatory cytokines. This pathway is represented only in Fig 3, A, and replaced by the word “SIGNAL” in Fig 3, B. A, Classic signaling, which is restricted to several cell types, is initiated through binding of IL-6 to the membrane IL-6R and forms a complex with gp130. B, Trans-signaling is driven by IL-6 in all gp130-expressing cells. Proinflammatory functions have been found to be mediated through binding of soluble IL-6R shredded from cells undergoing ADAM17-mediated apoptosis. C and D, IL-6 blockade therapy using a humanized anti–IL-6R mAb. A humanized anti–IL-6R antibody blocks IL-6–mediated signaling pathway by inhibiting IL-6 binding to the membrane (Fig 3, C) and soluble (Fig 3, D) receptors. ADAM17, A disintegrin and metalloprotease family protein; gp130, glycoprotein 130; IL-6R, IL-6 receptor; sIL-6R, soluble IL-6R; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription.