Figure 1.
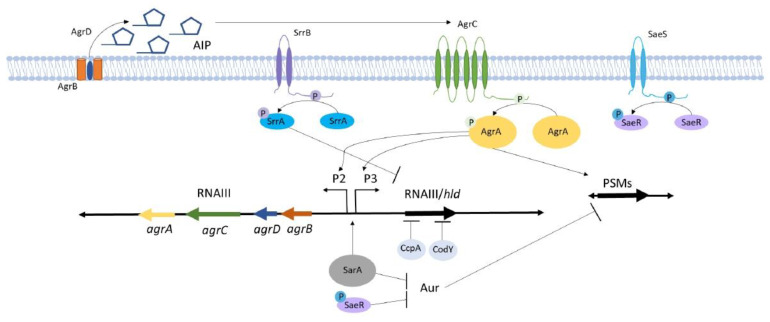
Accessory gene regulator (Agr) signals through self-regulation and crosstalk with other two-component systems. Quorum-mediated Agr signaling is influenced by regulatory proteins, staphylococcal accessory regulator A (SarA), carbon catabolite control protein A (CcpA), and CodY and two-component systems, staphylococcal respiratory response AB (SrrAB) and Staphylococcus aureus exoprotein expression response regulator (SaeRS), which are responsive to oxygen (SrrAB) and nutrient availability (SaeRS), as well as host immune stress. AgrB facilitates the formation of extracellular AIP from the AgrD precursor. Agr signaling occurs through AIP-mediated signal transduction at a threshold concentration that activates AgrC phosphotransferase activity to phosphorylate AgrA. AgrA activates the transcription of RNAIII via P3 to produce virulence factors implicated in S. aureus acute osteomyelitis. AgrA binding to P2 results in transcription of RNAII, leading to additional agrA, agrC, agrD, and agrB mRNA. Phosphorylated AgrA also enhances the transcription of phenol-soluble modulins (PSMs) directly. SarA and activated SaeR indirectly augment PSM production via inhibition of the protease Aureolysin (Aur).