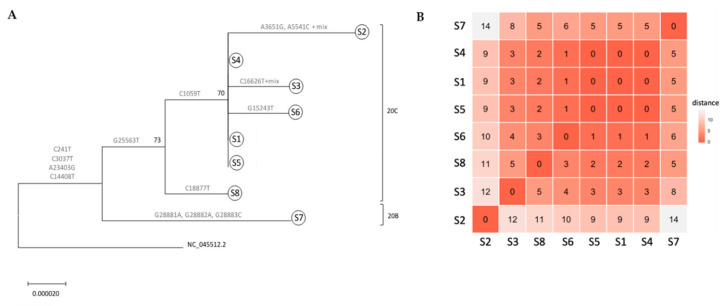
Figure 1.
Whole genome-based phylogenetic tree of ICVL local outbreak. (A) Phylogenetic tree of six ICVL samples (S1–S6), two family-related samples (S7–S8) and SARS-CoV-2 reference sequence (NC 045512.2). Tree was inferred by maximum likelihood based on the GTR + I + G evolutionary model. The robustness of branching pattern was tested by 1000 bootstrap replications and the percentage of successful bootstrap replicates is indicated at the nodes, where only values of >70% are shown. Mutational positions separating the samples are shown by each branch and corresponding 20B and 20C clades (according to Nextstrain nomenclature) are indicated. (B) Sample similarity clustering, calculated according to hamming distance (the number of different nucleotides across the whole genome sequences calculated for each pair of samples). Red represents the least difference and white the most. The number of differences is also noted.