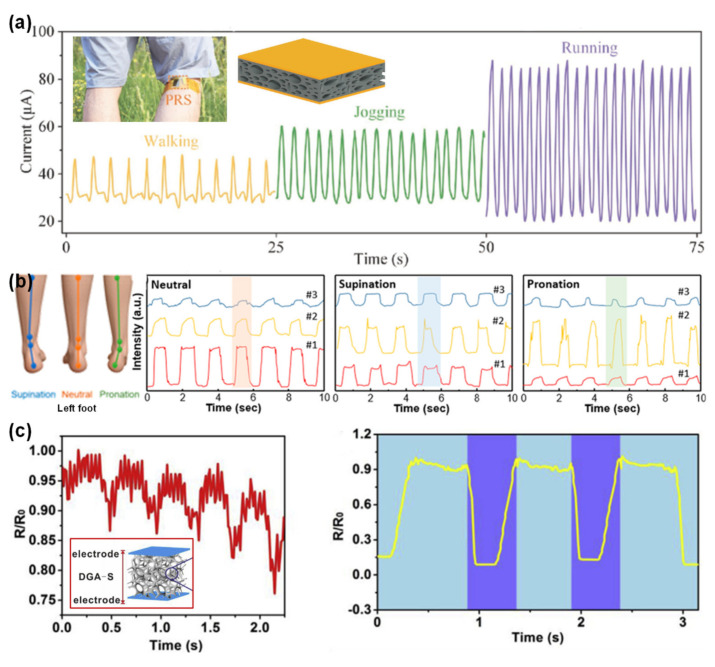
Figure 15.
E-skins applied to detection of walking or other related patterns. (a) Output of the e-skin developed by Haixia Zhang and co-workers in 2017 for walking, jogging, and running, with the insets showing the placement of the e-skin in the back of the leg and an illustration of the e-skin [232] (© 2020 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany). (b) Output of the e-skin developed by Tian-Ling Ren and co-workers in 2018 for the discrimination of neutral, supination, and pronation gait patterns (reprinted with permission from [168]. Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society, Washington, WA, USA). (c) Output of the e-skin developed by Jing Li and co-workers in 2018 for the detection of the motion caused by the Restless Legs Syndrome (left) or walking (right), with the inset illustrating the e-skin [195] (© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.).