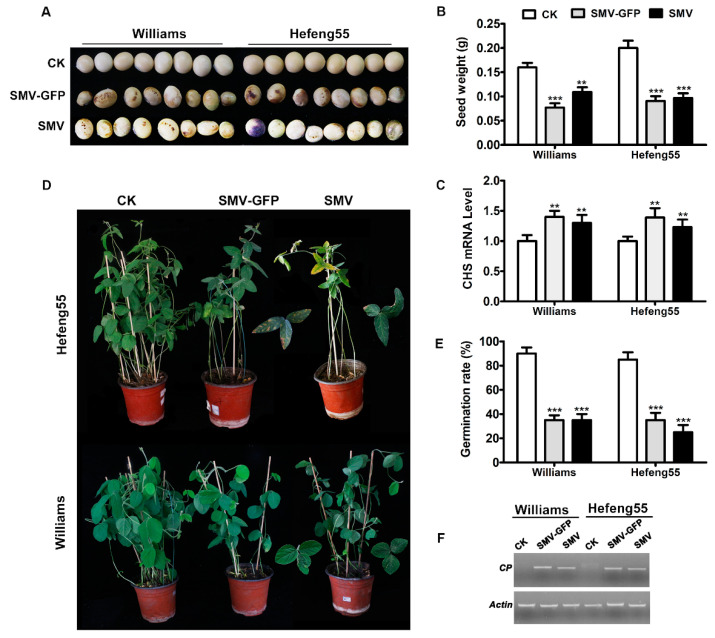
Figure 4.
Seed transmission of SMV derived from infectious clones. (A) Visual appearance of seed mottling upon infection with SMV derived from infectious clones. (B) Weight of the seeds showing mottling upon infection with SMV from infectious clones. T-test was performed between treatment and control group. Double asterisks, p < 0.01, Triple asterisks, p < 0.001. (C) CHS mRNA level determined by RT-qPCR assay in mottling seeds. Soybean actin gene expression was used as an internal control. (D) Phenotype of SMV-infected progeny seedlings. The mottling seeds were germinated in soil pots, and the phenotype was observed at 35 days. (E) Germination assay of SMV-infected seeds. The mottled seeds were germinated in soil pots, and the germination rate was calculated at 20 days. (F) SMV-specific RT-PCR analysis of progeny plants from SMV seed transmission. The internal reference gene actin was used as a control. The average number and SE value in each treatment group are shown. Statistical differences between SMV-infected and the control group were evaluated. Double asterisks indicate a significant difference at p < 0.01, and triple asterisks indicate a significant difference at p < 0.001.