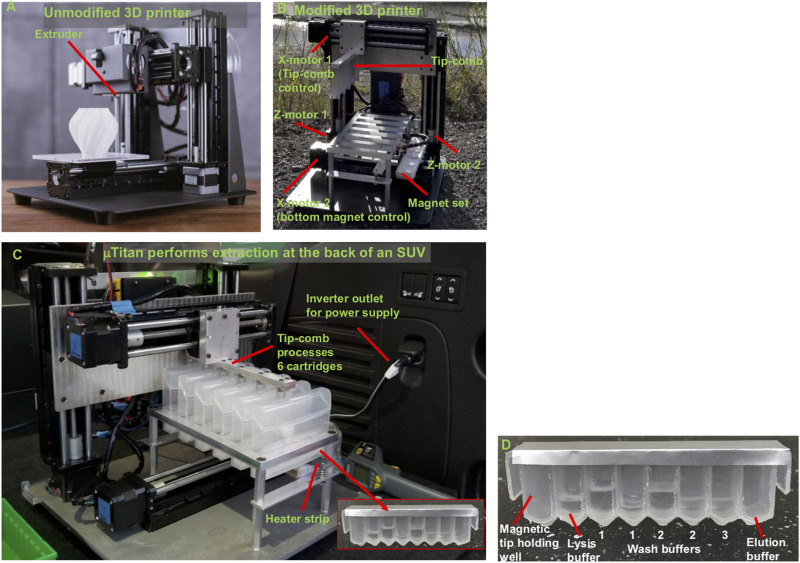
FIGURE 1.
Concept of converting a low-cost 3D printer to perform rapid and automated NA isolation. (A) A typical FMD type 3D printer. (B) A 3D printer turned extraction device. The extruder of a 3D printer was removed to allow the adaptors to be mounted. The magnetic particle processing tip-comb (tip-comb) was attached on the mount. Its vertical and lateral movements are controlled by two Z-motors and one upper X-motor controls. Another X-motor control below the extraction cartridges enable resuspension of magnetic particles for NA binding and washing (see description later). The tip-comb has 6 fingers with each finger has magnets to use magnetic coupling to externally control the extraction tips inside an extraction cartridge to perform extraction. There is no direct contact between the magnets, the samples, and MPs. Six samples can be processed simultaneously under the same protocol program. The heated strip under the elution wells uses the 3D printer’s extruder heater and thermistor to provide precise temperature control for heated NA elution. (C) μTitan placed inside the cargo area of an SUV. (D) A reagent strip that has been pre-filled with the appropriate extraction reagents.