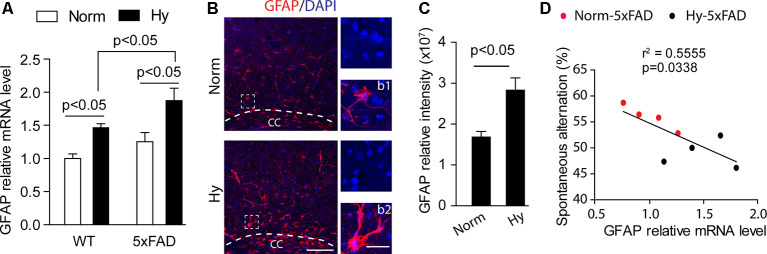
Figure 6.
Antenatal hypoxia increased reactive astrogliosis in the brain cortex of 2-month-old 5xFAD offspring. (A) qRT-PCR of GFAP mRNA levels in the cortex of offspring exposed to normoxia or hypoxia. Student’s t-test was applied to each data set. n = 4. (B) Confocal images of brain slices from 2-month-old 5xFAD offspring exposed to normoxia or hypoxia stained with antibody against GFAP (red). DAPI stains nuclei (blue). Insert (b1) shows normal astrocyte and (b2) shows the reactive astrocyte. Scale bar: (B), 100 μm; (b1,b2), 20 μm. (C) Quantification of GFAP fluorescence intensity in the cerebral cortex with ×20 objective. Data are mean ± SEM. Student’s t-test was applied to each data set. In total, nine sections from three animals were used for analysis. (D) Regression analysis of the correlation between spontaneous Y-maze performance with GFAP relative mRNA level. Single data points are from 5xFAD normoxia (red) and hypoxia treated mice (blue).