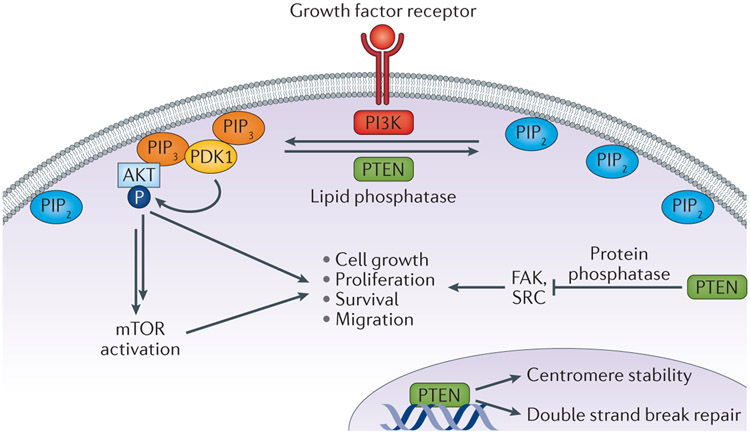
Figure 1 ∣. The diverse cellular roles of PTEN.
PTEN acts as lipid phosphatase, converting phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate [PI(3,4,5)P3 or PIP3] into phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PI(4,5)P2 or PIP2]. In this capacity, PTEN antagonizes the function of Class I PI3K activity, which converts PIP2 to PIP3. This lipid phosphatase activity of PTEN suppresses the activation of the downstream oncogenic AKT and mTOR signalling cascades. However, PTEN also has several other noncanonical functions, including weak protein phosphatase activity with known kinase substrates such as FAK and SRC. Finally, PTEN probably functions in the nucleus in a PI3K-independent manner to promote chromosome stability and DNA repair .