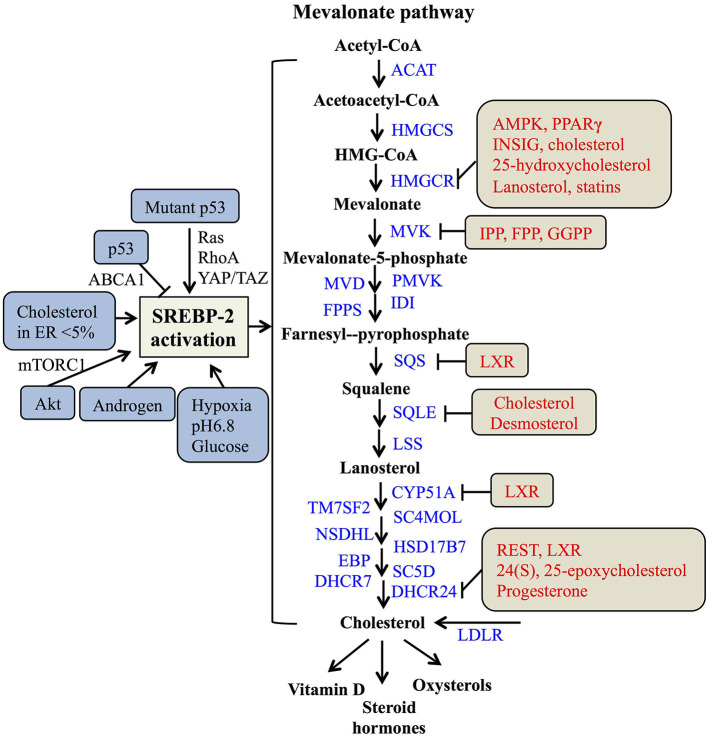
Figure 2.
The SREBP-regulated mevalonate pathway and its regulation. Schematic representation summarizing the SREBP-2-regulated mevalonate pathway and key enzymes for synthesis from acetyl-CoA to cholesterol and its products. Multiple signaling pathways such as p53, Akt, and androgen can regulate SREBP-2 activation. Several regulatory feedback mechanisms exist for different enzymes by various signals and mevalonate metabolites, such as cholesterol, IPP (Isopentenylpyrophosphate) and FPP (farnesylpyrophosphate). ACAT, acyl CoA-cholesterol acyltransferase; HMGCSm HMG-CoA synthase; HMGCR, HMG-CoA reductase; MVK, mevalonate kinase; MVD, HMG-CoA synthase; PMVK, phosphomevalonate kinase; IDI, isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase; FPPS, farnesylpyrophosphate synthase; SQS, squalene synthase; SQLE, squalene epoxidase; LSS, lanosterol synthase; CYP51A, lanosterol-14α demethylase; TM7SF2, steroid 14 reductase; SC4MOL, 4 methyl sterol oxidase; NSDHL, C3 sterol dehydrogenase; HSD17B7, 3-ketoreductase, EBP, phenylalkylamine Ca2+ antagonist binding protein; SC5D, sterol-C5-desaturase; DHCR7, 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase; DHCR24, 24-dihydrocholesterol reductase; LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptors; GGPP, geranylgeranylpyrophosphate; AMPK, adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor γ; INSIG, insulin-induced gene protein; LXR, Liver X receptor; REST, RE1-silencing transcription factor.