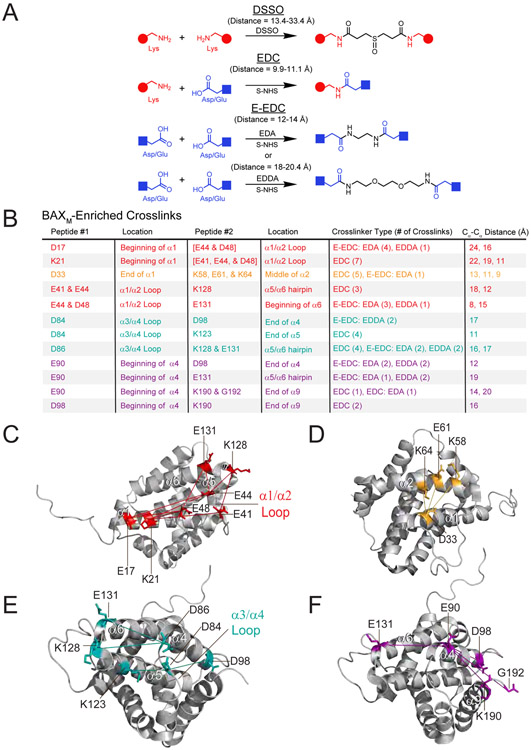
Figure 4. BAXM-enriched chemical crosslinks highlight the structural proximities lost upon formation of BAXO.
(A) Molecular structures, crosslinking reactions, and crosslink distance ranges (disuccinimidyl sulfoxide [DSSO], experimental; 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide [EDC], extended [E]-EDC, theoretical) of the chemical crosslinkers.
(B) BAXM-enriched (10-fold) crosslinks as determined by crosslinking acidic and lysine residues of BAXM vs. BAXO and mass spectrometry analyses. Crosslinked residues are colored according to their location on the BAXM structures below.
(C-F) Each of the identified crosslinks are compatible with the structure of BAXM (PDB: 1F16) and reveal the structural proximities in BAXM lost upon BAX oligomerization, including the adjacencies of (C) the α1-α2 loop with α1 and α6 (red), (D) α1 with α2 (orange), (E) α3/α4 with α5/α6 (cyan), and (F) α4 with α5/α6 and α9 (purple).
See also Data File S1.