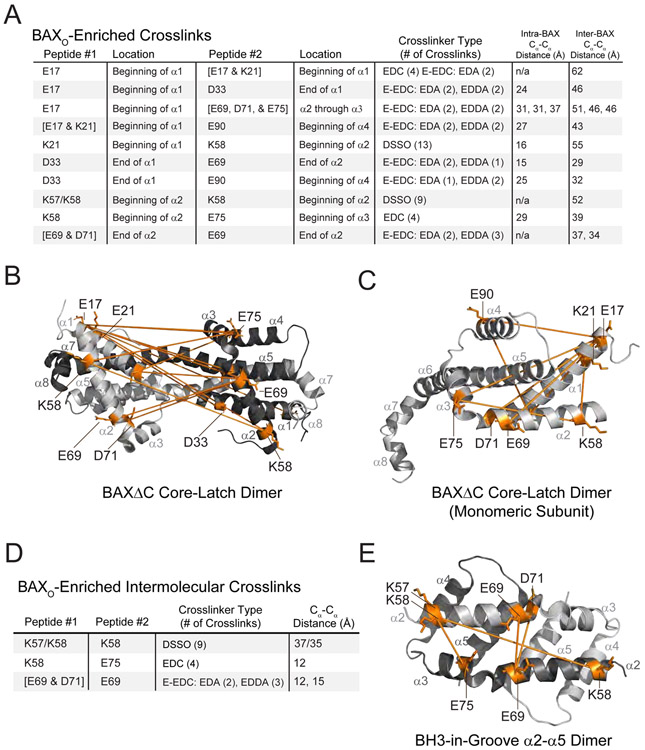
Figure 5. BAXO-enriched chemical crosslinks reveal structural proximity of the N-terminal and BH3 domain regions of oligomerized BAX.
(A) BAXO-enriched (10-fold) chemical crosslinks. Obligate intermolecular crosslinks between the indicated residues at the proximal portion of α1 and the proximal, middle, and distal portions of α2 highlights the adjacency of these structural regions in BAXO. Tabulated intra- and inter-BAX residue distances are based on the dimeric structure of BAXΔC (PDB: 4BD2).
(B-C) Mapping the BAXO-enriched crosslinks onto the BAXΔC dimer (PDB: 4BD2) as inter- (B) or intra- (C) molecular amino acid proximities (orange lines) demonstrates that the structure of BAXO is distinct from the off-pathway dimer, which violates the distance constraints of BAXO crosslinks.
(D) BAXO-enriched (10-fold) intermolecular crosslinks highlight the proximity of BAX BH3 domains in oligomerized BAX. Tabulated inter-BAX residue distances are based on the GFP-BAX α2-α5 dimer (PDB: 4BDU).
(E) Mapping BAXO-enriched intermolecular crosslinks onto the GFP-BAX α2-α5 dimer (PDB: 4BDU) reveals inter-residue distances (orange lines) that are compatible with (K58-E75, E69-E69, D71-E69) and violate (K57-K58, K58-K58) the distance constraints of BAXO crosslinks.
See also Data File S1.