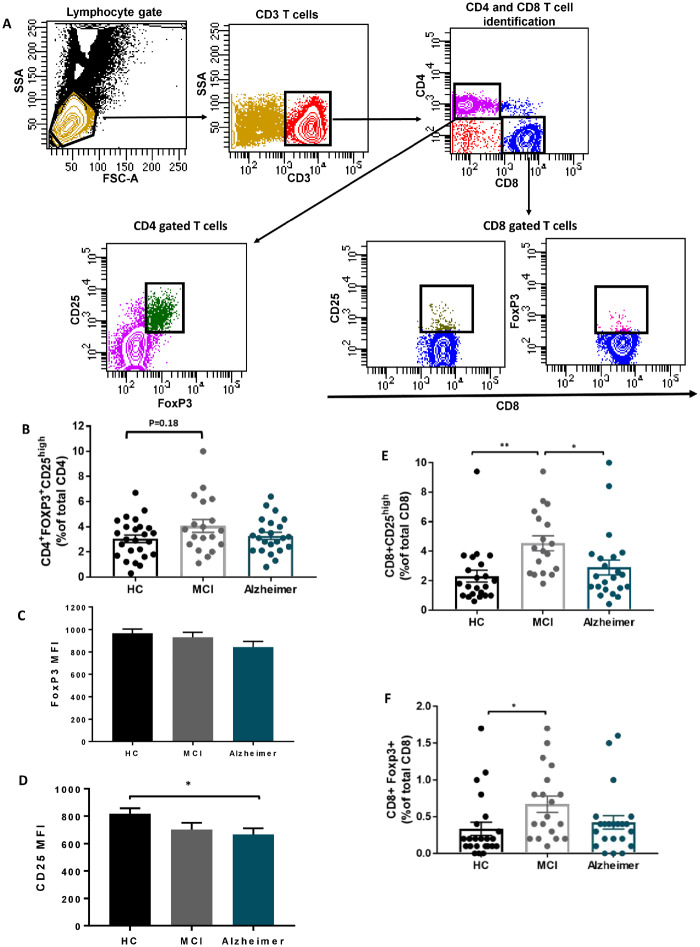
Figure 1.
Suppressor T cells immunophenotype in Alzheimer disease. (A) Gating strategy to identify CD4 and CD8 suppressor T cells; lymphocytes were delineated by forward/side scatter gating. CD3 were used to identify T cells among the previously selected viable lymphocytes. CD4 T cells and CD8 T cells were identified as uniquely expressing CD4 or CD8 antigens. Tregs were defined as CD4 T cells co-expressing CD25 and FOXP3. The expressions of CD25 and FoxP3 were then determined on CD8 T cells. (B) CD4+FOXP3+ CD25high T-cell percentage (% of total CD4), did not differ among HC, MCI and Alzheimer groups. (C) FoxP3 mean fluorescent intensity in CD4+FOXP3+ CD25high cell population was comparable among the three groups. (D) CD25 mean fluorescent intensity in the CD4+FOXP3+ CD25high cell population was reduced in Alzheimer dementia stage. (E, F) The percentages of CD8+CD25high and CD8+FOXP+ suppressor T cells (% of total CD8) were increased in MCI patients, compared with HCs. CD8+CD25high T-cell population differs significantly between MCI and Alzheimer. P-values are *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.