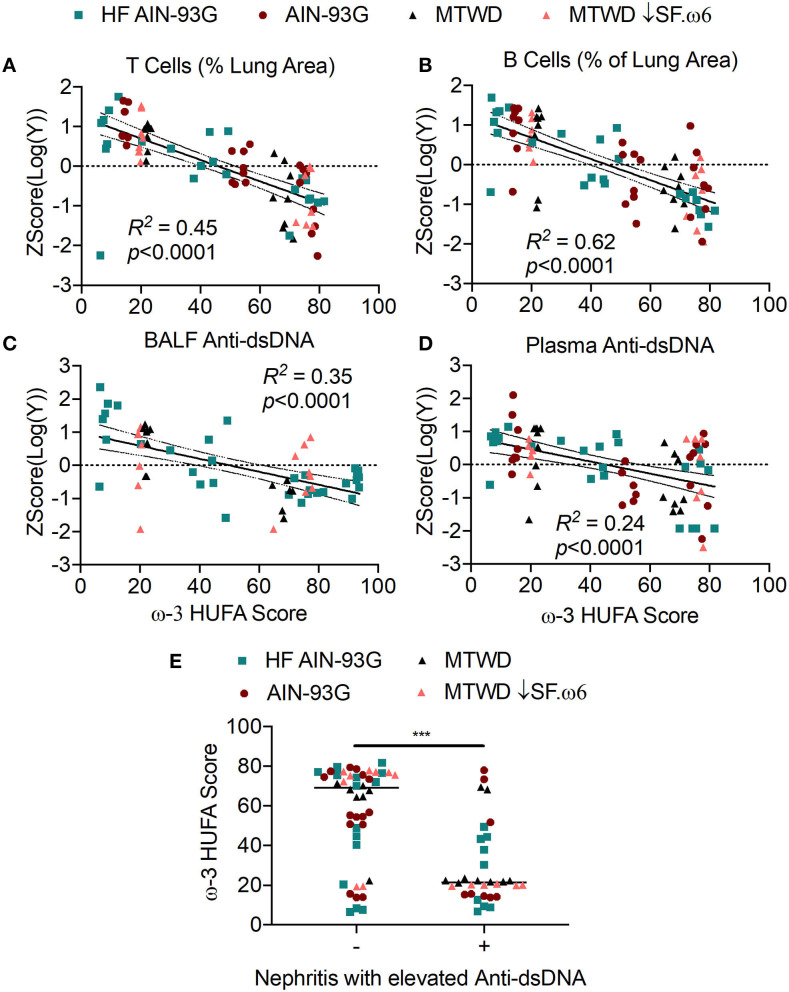
Figure 6.
High RBC ω-3 HUFA scores correspond with suppression of ectopic lymphoid structure (ELS) neogenesis, anti-dsDNA response, and disease progression in cSiO2-triggered NZBWF1 mice. (A,B) ELS neogenesis was assessed by measuring the volume density of (A) T cells (CD3+) and (B) B cells (CD45R+), respectively, in the bronchial and perivascular regions of the lung. Anti-dsDNA was measured in (C) BALF and (D) plasma by ELISA. Percent area covered by T or B cells and anti-dsDNA levels and were log10 transformed to normalize followed by autoscaling to standardize across experiments. These values were plotted against the ω-3 HUFA score and the resulting data analyzed by simple linear regression. Goodness of fit of the linear regression was presented as R2. Regression coefficients were considered statistically significant at p < 0.05. Shaded bands around regression lines represent 95% confidence intervals. (E) Mice positive for renal lesions and elevated plasma anti-dsDNA IgG (significantly different from mean of the Veh-treated group, p < 0.05) had significantly lower median ω-3 HUFA scores than mice in the the group negative for these endpoints, as assessed by the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U-test (***p < 0.001). Quantification of renal histopathology score was based on the following scoring criteria: No proteinosis, normal glomeruli (0); multifocal segmental proliferative glomerulonephritis (1); multifocal segmental proliferative glomerulonephritis and occasional glomerular sclerosis and crescent formation (2); diffuse global segmental proliferative glomerulonephritis (3). Animals receiving any score ≥1 were categorized as positive for renal lesions.