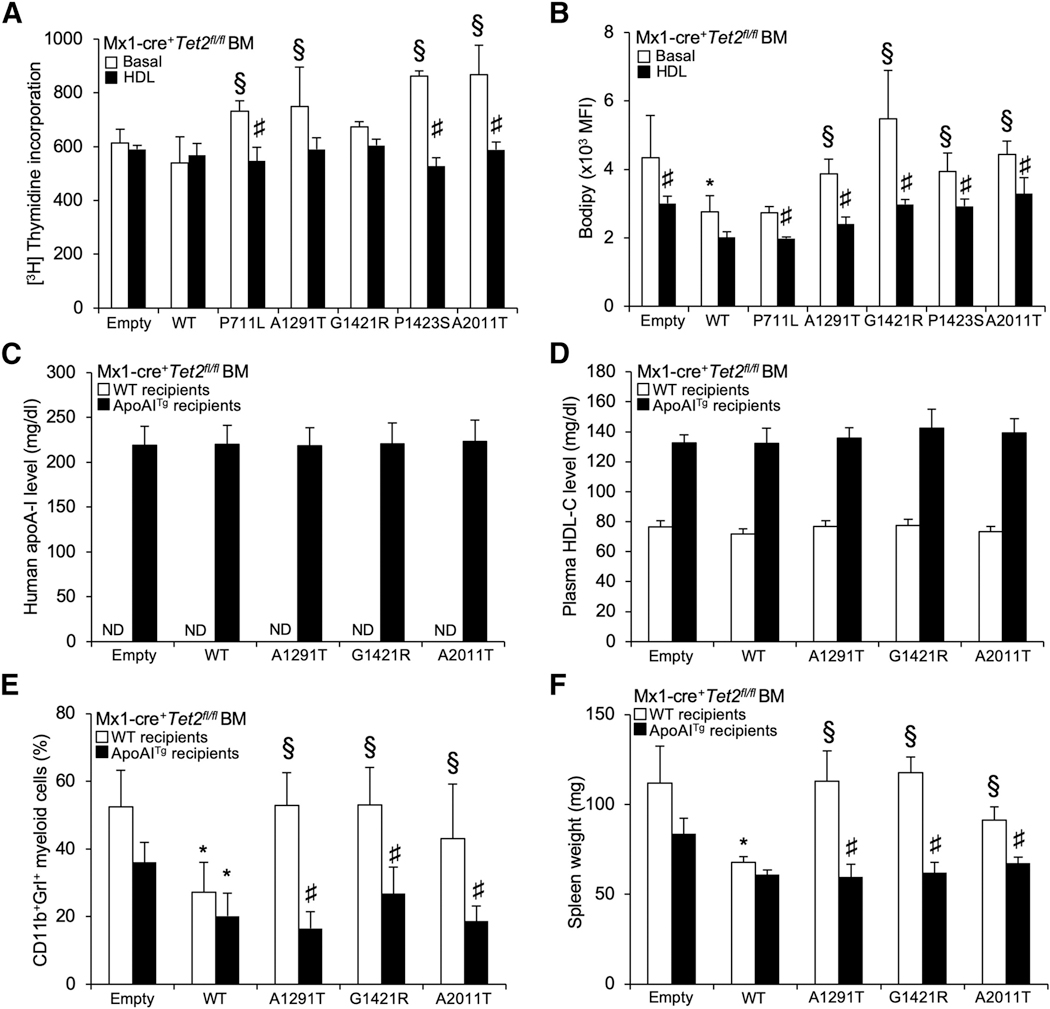
Figure 6. HDL Overcome Loss-of-Function ABCA1 Mutants and Limit the Myeloproliferative Disorder Induced by These Mutants in Tet2-Deficient Mice.
(A) Proliferation rates were determined after 2 h [3H]-thymidine pulse labeling in BM cells from empty, ABCA1-WT, and ABCA1 mutant-transduced animals on a Tet2-deficient background that were grown for 72 h in liquid culture in the presence or absence of 50 (μg/mL polyethylene glycol (PEG)-HDL.
(B) The quantification of BODIPY staining was determined by flow cytometry in these cells and expressed as the MFI. The results are means ± SEMs of cultures from at least 3 independent mice.
(C and D) Levels of human apoA-1 (hApoA-1) (C) and plasma HDL-cholesterol levels (D) were determined in WT or apoA-1 transgenic recipient mice transplanted with Mx1-Cre+Tet2fl/fl BM transduced with lentiviral particles expressing ABCA1-WT or ABCA1 mutants or empty vector.
(E and F) Peripheral blood CD11b+Grl+ myeloid subsets (E) and spleen weight (F) were quantified at the end of the study period (i.e., 7 weeks post-poly(l:C) injection that followed a 5-week recovery period post-BMT) in WT or apoA-1 transgenic recipient mice transplanted with Mx1-Cre+Tet2fl/fl BM transduced with lentiviral particles expressing ABCA1-WT or ABCA1 mutants or empty vector. Results are means ± SEMs of 4–5 animals per group.
*p < 0.05 versus empty control-transduced animals on a Tet2-deficient background. §p < 0.05 versus ABCA1-WT. #p < 0.05 versus non-HDL-treated conditions or transduced animals on a non-ApoA1Tg background.