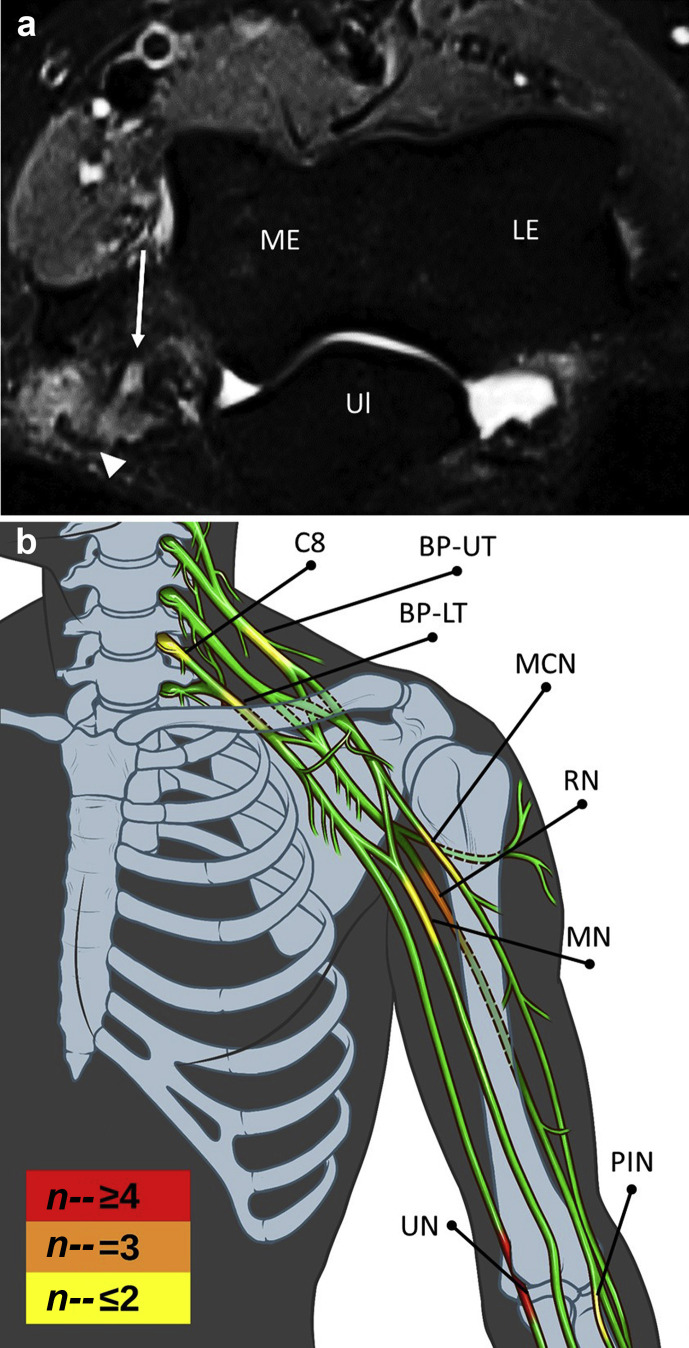
Fig. 1.
Locations of upper limb peripheral nerve injuries associated with prone positioning of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). (a) Axial STIR image from magnetic resonance neurography of the left humerus (Patient 5) demonstrates focal signal hyperintensity of the ulnar nerve (arrow) with focal adjacent soft tissue oedema (arrowhead). (b) Graphical summary of all upper limb PNI sites in this report. Heat map represents the frequency of PNI at defined anatomical sites. BP-LT, lower trunk of brachial plexus; BP-UT, upper trunk of brachial plexus; C8, C8 nerve root; LE, lateral epicondyle; MCN, musculocutaneous nerve; ME, medial epicondyle; MN, median nerve; RN, radial nerve; PIN, posterior interosseous nerve; PNI, peripheral nerve injury; STIR, short tau inversion recovery; Ul, ulna; UN, ulnar nerve.