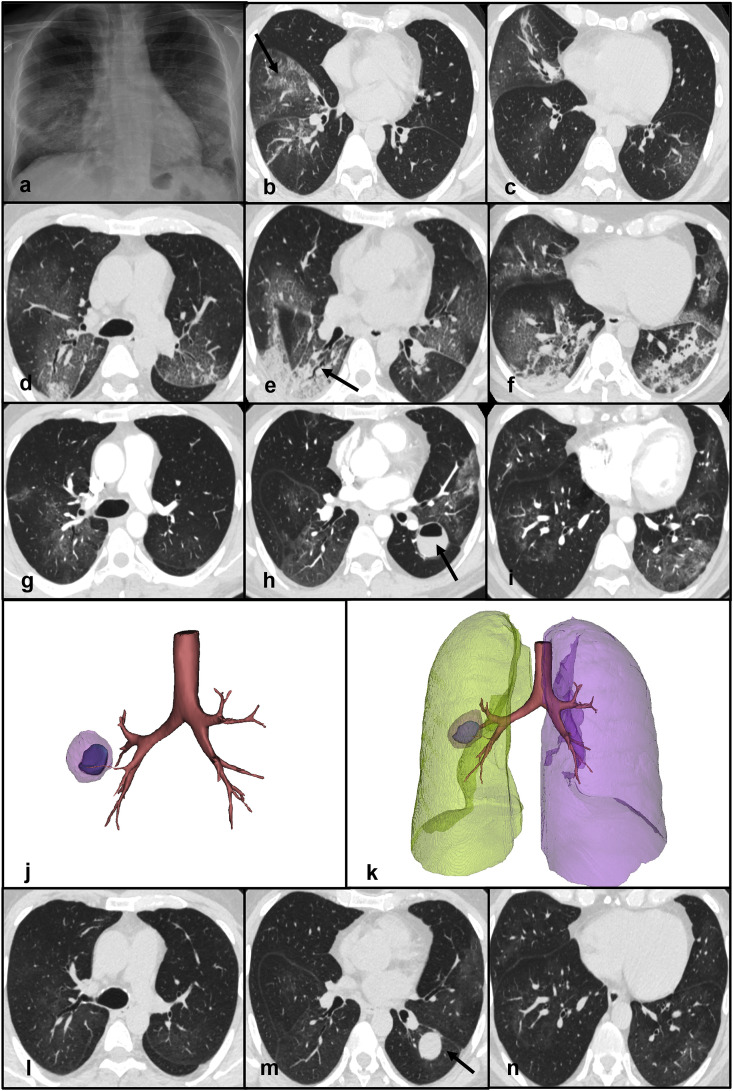
Fig. 1.
Panel a - Frontal chest X-ray demonstrating subtle, bilateral opacities mainly involving the mid and lower zones of the lungs. Panels b, c - Non-contrast chest CT scan showing multiple ground glass opacities and “crazy-paving” pattern (arrow - panel b) in the right middle and lower lobes. Panels d, e, f - Non-contrast chest CT scan documenting increased extent of GGOs mixed with new areas of consolidation in the lower pulmonary lobes. An air bronchogram is visible in the right lower lobe (arrow - panel e). Panels g, h, i - Contrast CT scan showing a lung abscess containing an air-fluid level in the superior segment of the left upper lobe (arrow - panel h). GGOs and consolidative areas are significantly decreased compared to the previous CT scan. Panels j, k - 3D reconstructions of the lung abscess. Panels l, m, n - Non-contrast chest CT demonstrating the lung abscess (arrow - panel m) and the near resolution of the parenchymal abnormalitiesAbbreviations
CT: computed tomography; GGO: ground-glass opacities.