Figure 4.
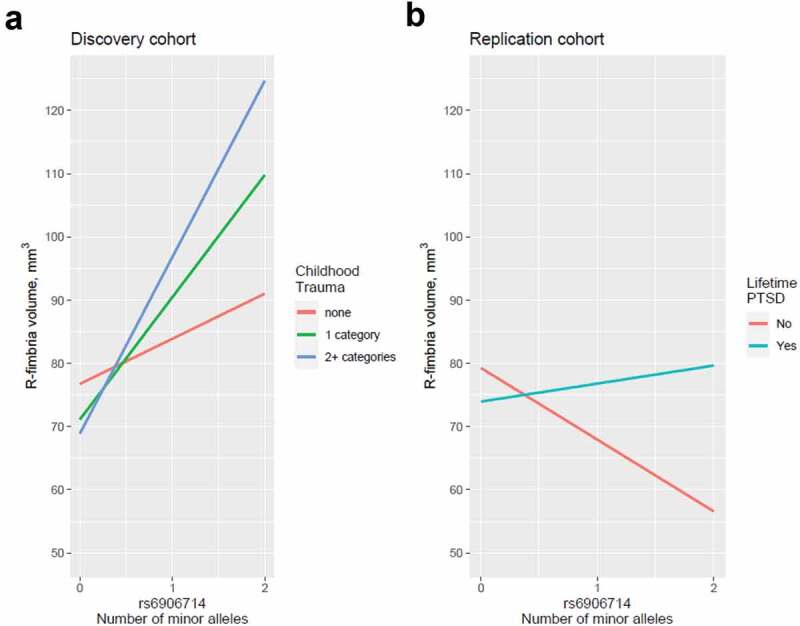
(a) Interaction between rs6906714 and childhood trauma affecting R-fimbria volume (p = 0.022). As exposure to childhood trauma increased, the effect of rs6906714 genotype on R-fimbria volume became stronger. Individuals who did not experience any childhood trauma, the association between rs6909714 genotype and R-fimbria was modest (p = 0.037; beta = 9.272 mm3). Individuals who experienced childhood trauma, the association was more robust with p = 0.0002; beta = 20.19 mm3 for 1 category of childhood trauma and p = 0.0002; beta = 25.19 mm3 for 2+ categories. There was no appreciable difference in the effect of rs6906714 genotype on R-fimbria volume among those who experienced 2+ categories of childhood trauma compared to those who experienced a single category. (b) Interaction between rs6906714 and lifetime PTSD on R-fimbria volume in the Grady cohort (p = 0.0421).
