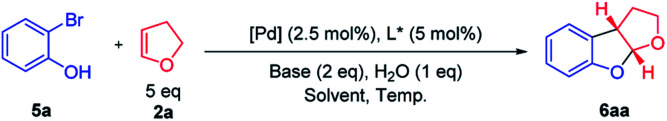
Table 2. Selective optimization of the carboetherification conditions a .
| |||||
| Entry | [Pd]/L | Base | Solvent | T (°C) | Yield b , c (ee) [%] |
| 1 | Pd2(dba)3/L3 | NaOtBu | Toluene | 80 | 40(87) |
| 2 | Pd2(dba)3/L3 | NaOPh | Toluene | 80 | 30(38) |
| 3 d | Pd2(dba)3/L3 | NaOtBu | DCM | 80 | 45(33) |
| 4 | Pd2(dba)3/L3 | NaOtBu | Toluene | 20 | 55(95) |
| 5 | Pd A/L3 | NaOtBu | Toluene | 20 | 51(95) |
| 6 | Pd2(dba)3/L5 | NaOtBu | Toluene | 20 | 44(85) |
| 7 | Pd2(dba)3/L7 | NaOtBu | Toluene | 20 | 60(96) |
| 8 | Pd2(dba)3/L8 | NaOtBu | Toluene | 20 | 52(82) |
aUnless otherwise specified, all reactions were carried out with 5a (0.2 mmol), 2a (1 mmol, 5 eq.), a [Pd] source (0.005 mmol, 2.5 mol%), N-Me-Xiang-Phos (0.01 mmol, 5 mol%), base (0.4 mmol, 2 eq.), and H2O (3.6 μL, 1 eq.) in a solvent (1 mL, 0.2 M).
bYield of isolated product.
cDetermined by chiral HPLC.
dPd2(dba)3 was added to 5 mol%, and L3 was added to 10 mol%.
