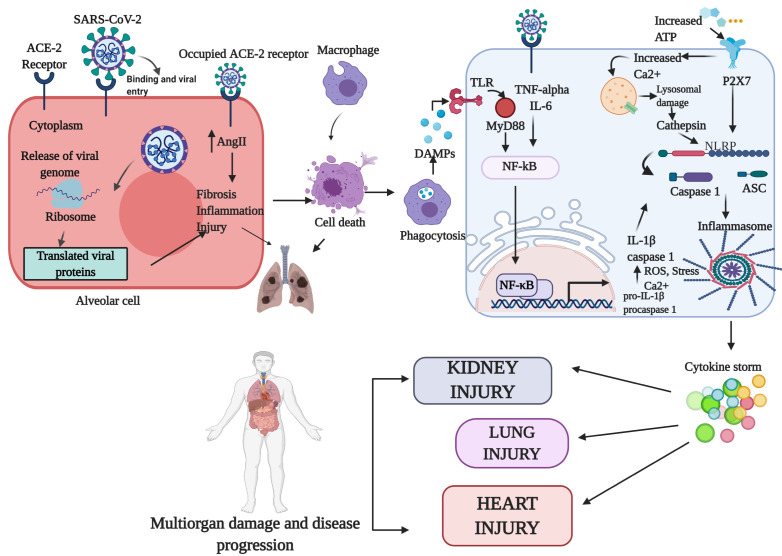
Fig. 1.
Role of cytokine storm in COVID-19. When SARS-CoV-2 binds the cell, the ACE2 receptors become occupied. This increases AngII which results in lung fibrosis, inflammation, and damage. The infected cell also undergoes cell death as a result of the viral in-fection. Macrophages engulf the dead cells and release DAMPSs, which bind the TLR and activated NF-κb by means of MyD88. Activated NF-κb binding activates the inflammasome. Binding of the virus to the receptor also upregu-lates IL-6 and TNF-αlpha, further activa-ting NF-κb. Increase in ATP binds the-P2X7 receptor, which in turn increases Ca2+, which causes lysosomal damage and further activation of the inflamma-some. Continuous activation of the in-flammasome produces the cytokine storm, resulting in multiorgan damage.