Figure 6. Exchanging inks in the vat for the multi-material VP printing.
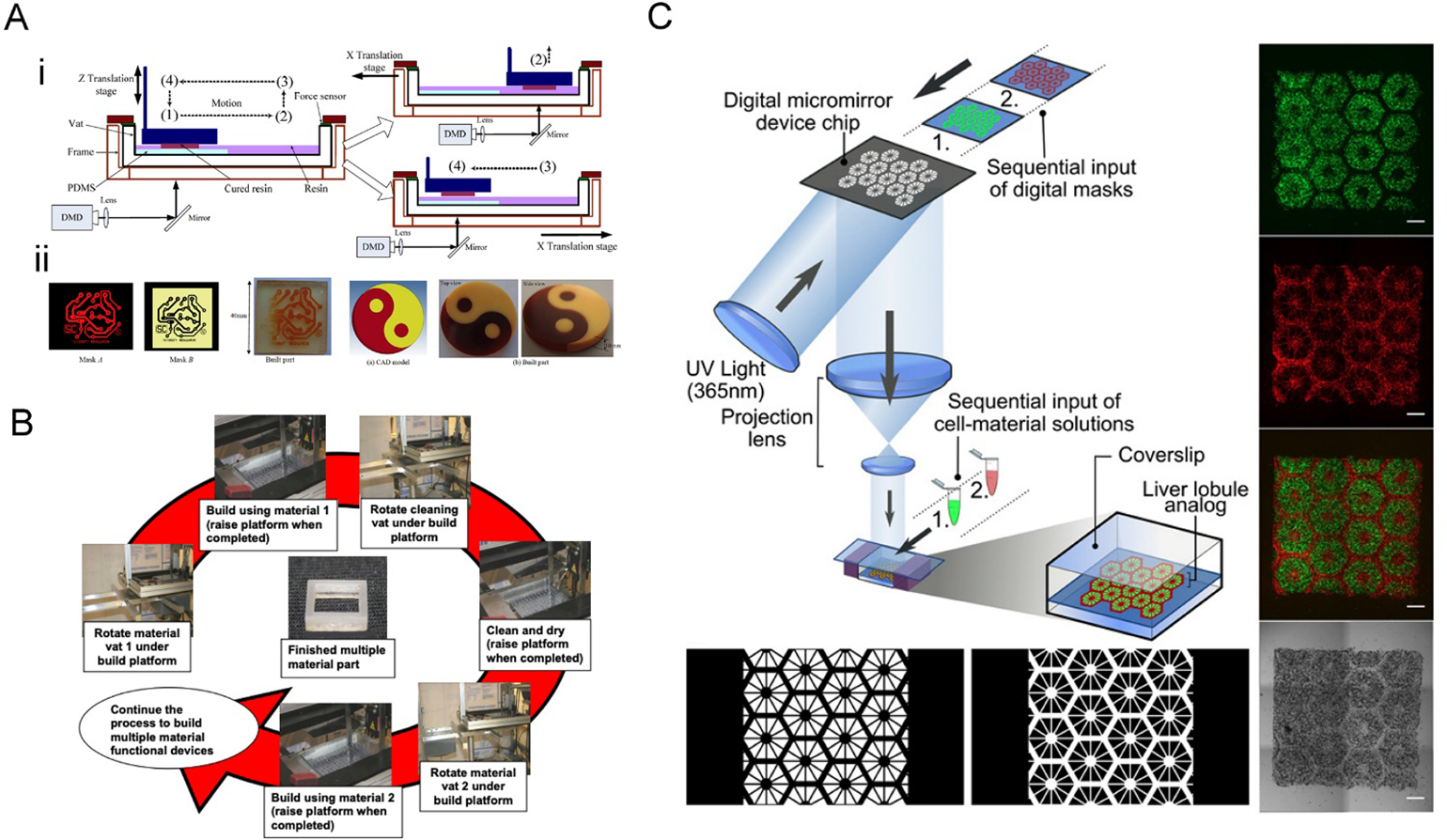
A) The two-channel multi-material DLP printing platform. i) The vat was divided into two channels, and only the printing channel with the PDMS film would be exposed to the images. After the photocrosslinking at position (1), the vat was moved to position (2), followed by elevating up and backing to the position (4) for the next layer of curing. ii) Examples of printed multi-material constructs. Reproduced with permission.[59] B) Operational principle of a multiple material stereolithography (MMSL) system. The print platform is submerged into the vat with the first ink to finish the first pattern fabrication; after raising the platform, a cleaning vat is rotated to clean the platform; then the print platform is lifted out from cleaning vat after cleaning and drying, and the vat with the second ink is rotated under the build platform. Reproduced with permission.[70] C) DLP-bioprinting of a vascularized hepatic model by sequentially inputting two different bioinks. The lobule structure was bioprinted with hiPSC-derived hepatic progenitor cells[26] and the sinusoids with HUVECs and ADSCs (red). Reproduced with permission.[71]
